mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Poland
- parliamentary-presidial republic
- own name: Rzeczpospolita Polska
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Historical Maps
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Kashubia
• Flags of the Voivodeships

National and state flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)






Merchant flag and state flag with coat of arms,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)






Naval and war flag,
ratio = 10:21,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




since 1993,
Naval jack,
ratio = 4:5,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




Flag of the Navy,
ratio = 10:21,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL), using:
Naval_Ensign_of_Poland2.svg: Mboro,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Army,
ratio = 10:21,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL), using: Kpalion,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 10:21,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL), using:
POL_Wojska_Lotnicze.svg: Poznaniak: Mboro,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Air Force air fields,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




Flag of the Navy air fields,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




Flag of the border patrol,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)



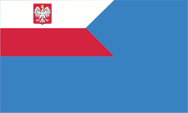
Flag for aux ships,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




since 1990,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 5:6,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Minister of Defence,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)



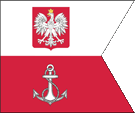
Flag of the Supreme Commander of the Navy,
ratio = 5:6,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)





1569–1795,
Flag of the Kingdom of Poland-Lithuania,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1587–1648,
Flag of the Wasa Kings,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1697–1763,
Flag of the Kingdom of Poland,
Source, by: Die Flag of Sachsen-Polen




1807–1815,
Flag of the Duchy of Warsaw,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1815–1846,
Flag of the Free State of Krakau,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




1815–1886,
Flag of the Prussian Grand Duchy/Province of Posen,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




1815–1831,
Congress Poland,
Flag of the Kingdom of Poland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




1815–1830,
Congress Poland,
Flag of the King of Poland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




1928–1939,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 5:6,
Source, by: Flags of the World



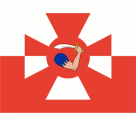
1919–1939, 1955–1980,
(in vermilion),
Naval jack,
ratio = 5:6,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)



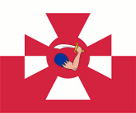
1919–1939, 1955–1980,
(in crimson),
Naval jack,
ratio = 5:6,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)



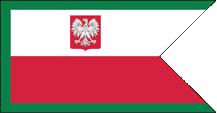
1980–1990,
(1953–1980 in vermilion),
Flag of the Border Defence Forces,
ratio = 10:21,
Source, by: Wikipedia (PL)




The flag of Poland shows two horizontal stripes in white and red. The colours have its roots in the Polish heraldry (white eagle on red ground). It was introduced on 5th of November in 1916, but it was already used in the 19th century at national uprisings. The beginning of the typical Polish heraldry with the white eagle on red ground is nearly complete hide in the past. Probably was this heraldry orientated – with the using of that colours – in the Frankish Empire and – with the using of the eagle – in the symbolism of the Roman Empire. The eagle appears for the first time on coins about the year 1000. Documentary and proved as coat of arms is it for the first time in the year 1295 on a deed of King Przemyslaw II. Other sources name also the years 1228 and 1241. In the time of the elective monarchy - from the 16th to the 18th century - each dynasty decided over the appearance of the flag of Poland, mostly flags with stripes in the colors red and white, or red flags with the Polish eagle. Interesting is the flag of Saxony-Poland, a period in which the Kingdom of Poland was ruled by the Saxon electors: 1697-1704, 1709-1733, 1733-1763. The flag showed two stripes in red and white, and in the middle a Polish eagle with the Saxon electoral coat of arms as a breastplate (For details: Die Flagge von Sachsen-Polen). The Polish state finished in the year 1795 with the last Polish Division as Poland became divided between Russia, Austria and Prussia. After Napoléon invaded that region (1806) he created the Duchy of Warsaw in the year 1807 which existed until 1815 under Saxon crown. It used a flag which showed two horizontal stripes in white and crimson. The Duchy of Warsaw became with the end of the era Napoléon divided between Prussia, Russia and the Free State of Krakau on the occasion of the Vienna Congress (29th of March 1815). The Prussian part became the Duchy of Posen which showed in its coat of arms the Polish eagle in the chest shield of the Prussian eagle, as well as a flag with two horizontal stripes in red and white. The Russian part was indeed called "Kingdom of Poland", but became known as "Congress Poland". The king was the Russian tsar and the country was not more then a Russian province. The Free State of Krakau (also Republic of Krakau) has only an area of ca. 155 sq.mi. It used until its annexation by Austria in the year 1846 a flag which showed two horizontal stripes in white and blue. During the First World War (1914–1918) Russian Poland was conquered by German and Austrian-Hungarian troops. The Russian rule ended here on the 5th of August in 1915 and on the 5th of November in 1916 was proclaimed the Regency Kingdom of Poland and it was adoped a flag which showed two horizontal stripes in white and red. By the Entente (Great Britain, France, Italy, USA) the Polish state was recognized not until 1917. On 7th of November in 1918 in Lublin was proclaimed the Republic of Poland and the since 1916 used flag became continued. In the beginning of the Second World War (1939–1945) Poland became overruned in only 26 days by German (since 1st of Sept.) and Soviet Russian troops (since 17th of Sept.) and has to capitulate on 27th of September in 1939. The State of Poland ended and became divided between the Soviet Union and the German Empire. On the occasion of the occupation by the Soviet Union in Lublin was established on 1th of January in 1945 a Polish government and the flag of 1916 became officially re-introduced and confirmed on 20th of March in 1956.
Source:
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Volker Preuß
The shade of red was initially not precisely defined. In 1921, the Polish military published the brochure "Coat of Arms and Flag of the Republic of Poland", which for the first time referred to the red as crimson, but without laying down a standard. In 1928, the President specified that the red was to be vermilion, but again without depositing a standard. On 31.01.1980, the shade was defined exactly for the first time, according to CIE, as x = 0.570, y = 0.305, Y = 16.0, ΔE = 8.0 and thus comes close again to the shade used until 1928.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)

Picture: Volker Preuß


since 1990,
Coat of arms of Poland,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4


ca.1000–1386 / 1569–1795,
Coat of arms of Poland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

1386–1569,
Coat of arms of Poland-Lithuania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

1815–1846,
Coat of arms of the Free State of Krakau,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1815–1832,
Congress Poland,
Coat of arms of the Kingdom of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1916–1918,
Regency Kingdom of Poland,
Coat of arms of the Kingdom of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1919–1927,
Coat of arms of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1927–1939,
Coat of arms of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1944–1980,
Coat of arms of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (PL)

1980–1990,
Coat of arms of the People's Republic of Poland,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

The coat of arms of Poland shows a golden armed silvery eagle on red field. That Polish heraldry has a long tradition and is proved as coat of arms for the first time in the year 1295 on a deed of King Przemyslaw II. Other sources name also the year 1241 or a portrayal without colours from the year 1228. Some coins keep suppose the use of the eagle even already about the year 1000. After the end of Poland in the year 1795 the Polish heraldry was revitalized in the year 1916. The coat of arms became modernized in 1927 and complyed at that time already nearly exact with the today’s design. After the end of the Second World War and the restoration of Poland were re-introduced the old symbols of the state in 1945. Involved by the potent influence of the Soviet Union Poland became a socialistic state. In this way occurs that in 1952 the crown was removed from the head of the eagle. After the end of the socialism the crown was put on the haed of the eagle again in 1990.
Source:
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Volker Preuß

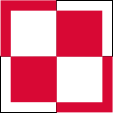
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Aircraft Roundel of the Border Guard,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
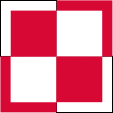
1921–1993
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
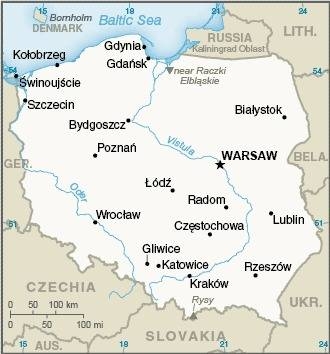
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 120.732 square miles, divided into 16 voivodeships
Inhabitants: 38.179.800 (2021), thereof 95,5% Poles, 0,28% Germans, 0,12% Ukrainians, 0,12% Belorussians (White Russians)
Religions: 86% Roman Catholic, 1% Protestant, 3% other Christian, 6% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 316 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Warsaw (poln. Warszawa), 1.794.166 inh. (2020)
official Language: Polish
other Languages: German, Ukrainian
Currency: 1 Zloty (PLN, Zl) = 100 Groszy
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source: Wikipedia (DE)

Lower Silesia
Kuyavia-Pomerania
Lódz
Lublin
Lubusz
Lesser Poland
Mazovia
Opole
Subcarpathia
Podlaskia
Pomerania
Silesia
Swietokrzyskie
Greater Poland
Warmia-Masuria
West Pomerania

4th to 2nd century B.C. · settlement of the today’s Poland by German (Goths, Burgundians, Vandals, Lugians) and Baltic nations (Pruzzians, Lithuanians, Lives, Kures), Slavic tribes settle the region of the today’s Ukraine and Belarus
4th to 6th century · Great Transmigration ("Migration Period"), because of the expansion of the Huns in the Middle Asia Region whole nations became pushed to west, the Huns push the Slavs and that the Teutonic tribes
6th to 7th century · massiv immigration of Slavic tribes (Polans, Masovians, Wislans, Pomorans) into the by Teutonic tribes inhabited regions of the today’s Poland, the Teutonic tribes migrate in western direction
ca.800–ca.900 · evolution of the Wislanic Principality of Krakau and the Polanic Principality of Gnesen
ca. 960 · Mieszko I. from the house of the Piasts becomes Duke of the Polans
ca. 1000 · Boleslaw I. from the house of the Piasts conquers the todays southern Poland
1119 · Boleslaw III. from the house of the Piasts conquers Pommerellen
1122 · Boleslaw III. from the house of the Piasts conquers Pommerania
1138 · war of succession after the death of Boleslaw III., disintegration of Poland in independent duchies, onset of the settlement by German farmers, Baltes invade from the north
1241 · Battle of Liegnitz, defeat of a Polish-German army under Duke Henry II. of Lower Silesia against the Mongols, Baltes invade from the north deeper
1226 · Conrad Duke of Masovia calls for the Teutonic Order to repulse the Baltes
1276 · Przemysl II. unifys the Duchies of Posen, Gnesen and Kalish and becomes Duke of Great Poland
1295 · Przemysl II. becomes crowned to the Polish King in Gnesen
1309 · the Teutonic Order occupies Pommerellen and the City of Danzig
1327 · Silesia becomes a Bohemian fiefdom
1370 · the lineage of the Piasts vanishes with Kasimir III. in the Kingdom of Poland
1370 · Ludwig I., King of Hungary, becomes King of Poland
1386 · Hedvig (Yadviga), daughter of Ludwig I. King of Hungary and Poland, marrys the Lithuanian Grand Prince Yagiello and establishes in this way the Polish-Lithuanian Personal Union and the lineage of the Yagiellons
1410 · Battle of Tannenberg, defeat of the Teutonic Order against Poland-Lithuania, in this way prevention of a further expansion of the Teutonic Order into Lithuania
1411/1466 · Peace of Thorn, the Teutonic Order cedes Pommerellen, the Kulm Country, Western Prussia and Ermland to Poland-Lithuania
1440 · Wladyslaw III., King of Poland-Lithuania becomes King of Hungary
1471/1490 · Casimir IV., King of Poland-Lithuania, earns the crowns of Bohemia and Hungaria
29th of August 1526 · Turk's Battle near Mohács, death of Ludwig II., Bohemia and Hungaria come to the House of Habsburg
1569 · Lublin Union, Poland and Lithuania, hitherto in Personal Union become united
7th of July 1572 · death of Sigismund II. August, the last Yagiellon, the empire's parliament (Sejm) gets the right to elect the king
1573 · election of Henry from the French lineage of Valois to the King of Poland
1576 · election of Stefan from the Hungarian lineage of Báthory to the King of Poland
1587 · election of Sigismunds III. from the Swedish lineage of Wasa to the King of Poland
1632 · election of Wladyslaws IV. from the Swedish lineage of Wasa to the King of Poland, in the afteryears wars against Sweden, Russia and the Ottoman Empire
1648 · Ukrainian cossack revolt under Bogdan Chmielnizki, overthrow of King Wladyslaw IV., the Ukraine separates from Poland and commits to Russia
1697 · election of August II. (the Strong) Elector of Saxony to the King of Poland
1700–1721 · Nordic War, Denmark, Saxony, Poland, Russia, Prussia, Hannover against Sweden, Poland is frequently place of war and becomes devastated, it has to cede Livonia to Russia and East Prussia becomes a fiefdom of Brandenburg
1733 · death of King August II., in the afteryears elections of new kings, wars against the Ottoman Empire for the Ukraine and Podolia, losses and defeats, political, economical and cultural decline
1764–1795 · regency of King Stanislaus II. August Poniatowski, growing Russian influence
1772 · First Polish Division, to counteract the growing Russian influence in the Polish state protect Austria and Prussia broad Polish territories against the Russian pounce by its annexation, Prussia annexes West Prussia, Ermland, Pommerellen (without Danzig), the Kulm Country, the northern Kuyavia and the Netze Area, Austria annexes Galicia, the southern parts of the Districts of Krakau and Sandomir, the District of Reussen with Lemberg, Russia annexes all Polish territory eastern the Duena River and the Dnjepr River, in the afteryears the conditions in the country become conspicuously better, but the Confederation of Magnats (nobilitie's assembly) of Targowica in the year 1792 calls for Russian support
1793 · Second Polish Division, to counteract the growing Russian influence in the Polish state again protects Prussia once more broad Polish territories against the Russian pounce by its annexation, Prussia annexes Great Poland (South Prussia) and Danzig, Russia annexes the Ukraine, Eastern Polesia and Eastern Wolynia, as a result of that in 1794 occurs the national people's revolt under Tadeusz Kosciuszko which was especially orientated against the Russians and the pro-Russian aristocracy, once more political, economical and cultural decline
1795 · Third Polish Division, to counteract the more growing Russian influence in the Polish state again protect Prussia ans Austria once more broad Polish territories against the Russian pounce by its annexation, Prussia annexes New East Prussia (Masovia and parts of Lithuania), Austria annexes Little Poland (Western Galicia), Russia annexes all the remained Polish territory (Western Polesia and Western Wolynia, Lithuania and Courland), the existence of the Polish state finished
1806 · Germany Campaign of Napoléon I., defeat of the German Empire, end of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation
1807 · Prussia has to cede the since 1793 and Austria the since 1795 annexed regions to the by Napoléon created Duchy of Warsaw under King Frederick August of Saxony
1813/1814 · Battle of Nations near Leipzig, end of the era Napoléon
29th of March 1815 · Vienna Congress, reconfiguration of Europe after the era Napoléon, the Duchy of Warsaw becomes dissolved. Prussia earns back the Kulm Country, the Netze Area and the western part of Great Poland (Posen), Krakau becomes a Free State. All other regions of the former Duchy of Warsaw come as "Kingdom of Poland" (Congress-Poland) to Russia, Polish King is the Russian tsar and the country is not more then a Russian province
1830–1831 · by the Polish aristocracy instigated Polish nationalistic people's revolt ("Warsaw Revolt") in Russian Congress Poland and even in the Prussian Grand Duchy of Posen, the revolt becomes suppressed, the mainly in the Prussian Grand Duchy of Posen reigning Polish aristocracy becomes overthrowed and Posen becomes transformed in a Prussian province
1846 · out of the Free State of Krakau organizes the withdrawed Polish aristocracy a further nationalistic people's revolt in the Austrian Galicia, the revolt becomes suppressed, Austria occupies and annexes the Free State of Krakau to prevent further agitations on its territory
1863–1864 · Polish nationalistic people's revolt in Russian Congress Poland, the revolt becomes suppressed, in consequence of this the Kingdom of Poland becomes abolished and directly incorporated to Russia as "Vistula Land" (Priwislinskij Kraj)
1864 · abolition of the serfdom in Congress Poland
1914–1918 · First World War, November 1914 to August 1915: Russian Congress Poland becomes conquered by German and Austrian-Hungarian troops, 5th of August 1915 capitulation of the Russian troops in Poland
5th of November 1916 · proclamation of the Regency Kingdom of Poland, first under a crown marshal, from 1917 under a regency council
1917 · the Kingdom of Poland becomes recognized by the Entente (Great Britain, France, Italy, USA)
7th of November 1918 · proclamation of the Republic of Poland in Lublin, President Józef Pilsudski
1920 · Versailles Dictate, the German Empire loses Posen (50% German inhabitants) and West Prussia (65% German inhabitants), until 1939 become ca. 1.000.000 Germans and Jews banished out of Poland into the German Empire and ca. 20.000 of them become murderd
1926–1935 · presidial dictatorship of Józef Pilsudski
1932 · non agression pact with the Soviet Union
1934 · non agression pact with the German Empire
1938 · demands of the German Empire concerning Danzig and West Prussia and clarification of the minoritie's question, Poland rejects
1st of September 1939 · invasion of German and Slovak troops (3rd of September 1939 France and Great Britain declare the war to the German Empire, onset of the Second World War)
17th of September 1939 · invasion of Soviet-Russian troops in Eastern Poland
27th of September 1939 · capitulation of the Polish troops, the by the German troops conquered Territories of Posen, West Prussia, Danzig, New East Prussia become incorporated into the German Empire again, Little Poland and Galicia become summarized to the "General Government" (seat of administration: Krakau), the Polish eastern territories of Wolhynia and Podlesia become annexed by the Soviet Union, during the war between 1939 and 1945 lose ca. 4.500.000 Poles their lives
1st of August 1941 · Eastern Galicia (since 1939 occupied by the Soviet Union) becomes affiliated to the General Government
1st of August–2nd of October 1944 · "Warsaw Revolt", bloody suppressed
21st of July 1944 · in context of the occupation by the Soviet Union constituates in Chelm the communist committee of the National Liberation
1st of January 1945 · in Lublin constituates a pro-communist and pro-soviet provisional government
1945–1947 · affiliation of the Prussian Provinces of East Prussia, Pomerania, Silesia and further regions to the Polish state, expulsion of ca. 9.000.000 German inhabitants, ca. 1.300.000 of them become murdered or die during the flee
19th of February 1947 · new constitution
22nd of July 1952 · new communist constitution
1956 · worker's agitations, partial liberalization
1980 · worker's agitations, strikes, foundation of the "Solidarnosc" trade union
1981 · declaration of the status of war
1983 · abolition of the status of war
1989 · worker's agitations, strikes, changes in the constitution, partial free elections, permission and victory of the "Solidarnosc" trade union
1991 · free elections
1992 · new and democratic constitution
12th of March 1999 · Poland becomes a member of the NATO
2004 · Poland becomes a member of the European Union
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Weltgeschichte,
Discovery '97,
Schwarzbuch der Vertreibung,
Wikipedia (DE)

Clickable Map of the historical Territories in the Region
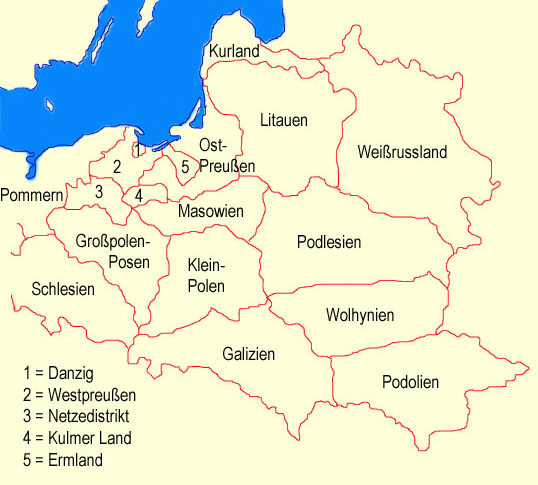
Map: Volker Preuß
Territorial evolution of Poland between 1721 and nowadays:
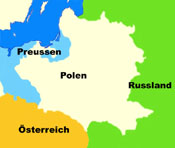
1721–1772
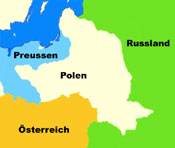
1772–1793
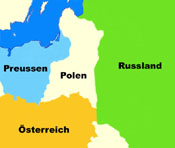
1793–1775
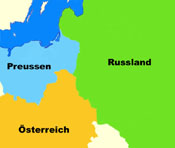
1795–1806
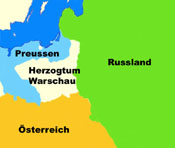
1807–1815
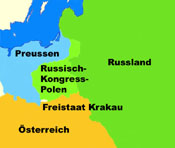
1815–1846
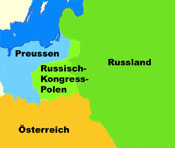
1846–1916
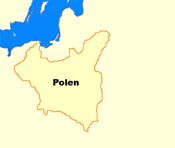
1920–1939
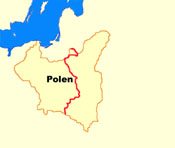
1939 (Division)
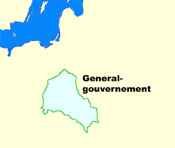
1941–1944
since 1945
Maps: Volker Preuß

The name "Poland" has its roots in the name of the Slavic tribe of the "Polans". This word Wort is coherent with the word "Polje" what means "field". A indication for the agrarian nature of the forefathers of the today’s Poles.
Source: Volker Preuß



![]()






























































