mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Romania
- presidial republic
- own name: România
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Flags of some Minorities
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, state, merchant and naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)






Naval jack,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Walachia and Moldavia:

1848–1859,
Unofficial national flag of the Romanians in Walachia and Moldavia



Principality of Romania, 1861–1881:

1861–1866,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1866–1881,
National and Merchant flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt






1862–1866,
Flag of the Prince,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1867–1872,
War flag and flag of the Prince,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1872–1881,
War flag and flag of the Prince,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Kingdom of Romania, 1881–1947:

1881–1947,
National and Merchant flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggenbuch 1939






1897–1902,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1902–1914,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1914–1921,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1922–1930,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1930–1940,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1940–1947,
Naval and War flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1921(?)–1947(?),
Merchant flag for naval reserve officers,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggenbuch 1939




1921–1947,
Naval jack,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggenbuch 1939



seit/since 1921,
Masthead pennant,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1881–1921,
Flag of the King,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1881–1921,
Flag of the Crown Prince,
Source, by: Flags of the World



1921–1947,
Flag of the King,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggenbuch 1939




1921–1947,
Flag of the Crown Prince,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flaggenbuch 1939




pilot flag (Pilot Call flag),
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
FOTW
This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is:
 Pilot on board
Pilot on board
 Call for Pilot
Call for Pilot



People's Republic of Romania, 1947–1965:

1948–1952,
National and Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



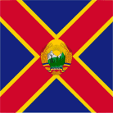
1948–1952,
Naval jack,
with changed coat of arms used to 1965
Source, by: Flags of the World




1948–1952,
Standard of the Presidium of the People's Republic,
with changed coat of arms used to 1965
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




1948–1952,
Standard of the Chairman of the Presidium of the People's Republic,
with changed coat of arms used to 1965
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




1948–1952,
Standard of a Minister,
with changed coat of arms used to 1965
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



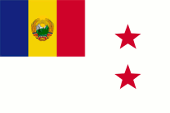
1948–1952,
Standard of the Minister of Defense,
with changed coat of arms used to 1965
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




1952–1965,
National und State flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Das farbige Flaggenlexikon




1952–1965,
Naval and War flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Das farbige Flaggenlexikon




1952–1965,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Das farbige Flaggenlexikon





Socialist Republic of Romania, 1965–1989:

1965–1989,
National, merchant and naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen




1965–1989,
Naval jack,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1965–1989,
Standard of the President and Chairman of the State Counsel,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




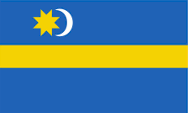
Flag of the National Council of the Székelys,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




Flag of the Székelys in the area of Csíkszék,
Source, by: Adam & Wikipedia (HU)




Coat of arms of the Transylvanian Saxons,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

The flag of Romania shows three vertical stripes in blue, yellow and red. The Romanian colours were created during the revolution of 1848/1849 by combining the colours of the Principality of Wallachia and the Principality of Moldavia, namely yellow/blue and red/blue. However, it seems that blue, yellow and red had already been used in Wallachia, and the official name of the Principality of Wallachia "Principatul Tării Românesti" also showed the use of the Romanian term. However, in 1861, the state of Romania was created by the union of these two principalities. Ostensibly nowadays the blue stands for the cloudless heaven above the country, the yellow for the wealth in mineral resources and the red for the courage of the Romanian people.
The first tricolor in the colours blue, yellow and red was created in 1848, the European Year of Revolution, but initially with horizontal stripes. That flag became officially recognized in 1859 and became in 1861 adoped for the State of Romania, but in the colours's sequence of red, yellow and blue. Since 1866 the flag arised by the example of the French tricolor with three vertical stripes in blue, yellow and red. The colours of the present flag were last defined by Law 75/1994 of 1995, but only as cobalt blue, chrome yellow and vermilion red, without specifying more precisely. This seems to have been defined from practice: Blue = Pantone 280c, Yellow = Pantone 116c and Red = Pantone 186c.
Important events for the flag history of the country that affected the design of the flags and coats of arms were: the proclamation of the kingdom in 1881, the establishment of the socialist system in 1947/1948 and the introduction of a democratic system in the year 1989. However, the national flag only bore a coat of arms in the times of socialism.
The sources for the historical flags are quite poor and they show different results. Even standard and general reference works use flags which obviously did not exist. This particularly affects the period before and during the Second World War. Back then, you probably had other problems than to ensure that your own flags are displayed correctly. One has the impression that the source situation has gradually improved and that some things can be better explained and supplemented retrospectively. This applies in particular to the naval and war flag, which in principle always had the same structure, ultimately differing only in the monogram of the respective king, which appeared in the four corners of the flag.
The most famous national minorities are the Székelys (sometimes called Hungarians, which is not entirely correct), the Transylvanian Saxons and the Banat Swabians. The Szekler are even in the majority in some regions of Transylvania, the Transylvanian Saxons have emigrated in large numbers and the Banat Swabians hardly exist in the Banat. The Székelys have their own flags, such as the flag of the National Council, a political organization whose flag goes back to the historical flag of the Székelys. Furthermore, there appears to be a red, gold and black flag. The Swabians and Saxons do not have their own flag, only coats of arms.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (EN),
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Volker Preuß


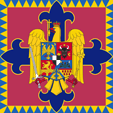
since 2016,
Coat of arms of Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)


1867–1872,
Coat of arms of the Principality Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1872–1881,
Coat of arms of the Principality Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1881–1921,
Coat of arms of the Kingdom Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1921–1947,
Coat of arms of the Kingdom Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1948–1952,
Coat of arms of the People's Republic Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1952–1965,
Coat of arms of the People's Republic Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1965–1989,
Coat of arms of the Socialist Republic Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1992–2016,
Coat of arms of Romania,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

The historic and even the modern blazon showed and show in their fields the heraldry of the landscapes and parts of Romania, always of Walachia (eagle) and of Moldavia (bull's head), since 1872 also of the Dobruja (two stylized dolphins) und since 1921 also of Siebenburgen/Transylvania (seven castles and eagle) and of the Banat (golden lion and golden bridge). Between 1872 and 1921 the blazon showed in its third field even the heraldry of Oltenia, a part of Walachia, a golden lion above a crown with a star between the paws. Between 1867 and 1947 was positioned amid the Romanian blazon a black and white squared central shield, the coat of arms of the Hause Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen. The big golden eagle with the cross in its beak was placed behind the blazon from 1921, which was hesupported by two lions between 1872 and 1947. The eagle held in its claws he the sword of Stephen the Great and the golden scepter, from 1992 the mace of Michael the Brave instead of the scepter. The eagle wore a crown until 1947 and then again from 2016.
In the year 1947 the monarchy was abolished and the people’s republic became proclaimed. That bolshevization was to see even in the heraldry because in 1948 was introduced a new coat of arms. It showed – surrounded by a wheat garland – a Romanian scenery with a river, forest, mountains and a derrick. In the year 1952 was added the red star of communism, and on the 21st of August in 1965 was added the name of the country into the colorful ribbons of the wheat garland. On the occasion of the overthrow of the communist dictatorship that coat of arms was removed from the flag and in principle not used anymore. Not until the September in 1992 was adoped a new coat of arms. It complys generally the until 1947 valid blazon, but the eagle carrys no crown anymore and the black-white central shield is lacking.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Volker Preuß

Position:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the Country:
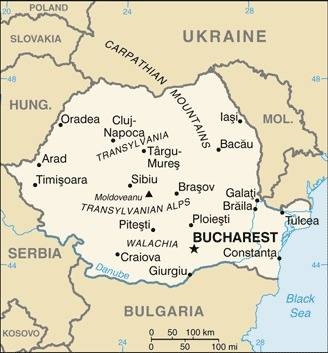
Source: CIA World Factbook
Historical Regions:
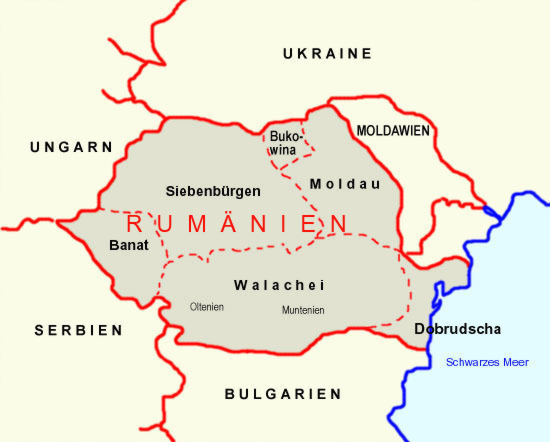
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: 92.043 square miles
Inhabitants: 19.520.000 (2018), thereof 89% Romanians, 7% Székelys (Hungarians), still ca. 36 000 Germans (Siebenburgen/Transylvanian Saxons and Banat Suebians), furthermore Gipsies, Serbians, Ukrainians, Croatians, Bulgarians, Slovaks
Density of Population: 212 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Bucharest (rum.: Bucuresti), 1.821.000 Ew. (2018)
official Language: Romanian
other Languages: Hungarian, German
Currency: 1 New Lei (L) = 100 Bani
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

ca. 2000 B.C. · evolution of the nation of the Thrakians in Dakia (today’s Siebenburgen/Transylvania)
7th century B.C. · foundation of greek colonies at the coast of the Black Sea
70–44 B.C. · legendary reign of the Thrakian King Burebista
ca. 10 A.D. · conquest of the Countryside of Dobruja by the Roman Empire, incorporation in the Province of Moesia
106 · the Roman Emperor and General Trajan conquers Dakia, incorporation as Province of Dacia
4th to 6th century · Great Transmigration ("Migration Period"), because of the expansion of the Huns in the Middle Asia Region whole nations became pushed to west, the Huns push the Slavs and that the Teutonic tribes, the Teutonic tribes switch over to the area of the Roman Empire
ca. 250 · gradual settlement of Siebenburgen/Transylvania by the Teutonic tribe of the Gepides
269 · the Teutonic Western Goth conquer the Dobruja
270 · the Roman troops retreat from Dacia
271/272 · the Roman Emperor Aurelian cedes Dacia officially to the Western Goth
441 · the Huns range Dacia and submit it
453 · death of Attila, the King of the Huns
454 · withdrawal of the Huns, evolution of the Empire of the Gepides in Siebenburgen/Transylvania
567 · Teutonic Langobards and Caucasian Awares conquer the Empire of the Gepides, Awares populate Siebenburgen/Transylvania
6th century · immigration of Slavs
7th century · out of the remaining Dako-Romans arises the Nation of the Dako-Romanesques
800 · annihilation of the Empire of the Awares by Carl the Great, Dacia is temporary ruled by Bulgarians
9th to 13th century · invasions of the Petsheneges, Kumans and Tatars
1000 · Siebenburgen/Transylvania comes under Hungarian control
12th century · the Hungarian king supports the settlement of Siebenburgen/Transylvania with German settlers
13th century · ein Volk der Rumänen wird erstmals urkundlich erwähnt
1300–1330 · unification of smaller Romanian principalities (Oltenia, Muntenia ...) to the Principality of Walachia
1359 · establishment of the Principality of Moldavia between the Carpathia Mountains and Dnjestr River during the battles against the Tatars
1387 · dependence from Poland-Lithuania
1400 · initial Turkish (Ottoman Empire) attacks against Moldavia and Walachia
1415 · the Principality of Walachia has to pay tribute to the Ottoman Empire (Turkey)
1455 · the Principality of Moldavia has to pay tribute to the Ottoman Empire (Turkey)
1461 · Prince Stephan III. of Moldavia (the Great, ca. 1435–1504) earns Walachia
1475 · revolt of the Principality of Moldavia under Prince Stephan the Great, triumph over the Turks, restoration of the independence of Moldavia and Walachia
1497 · Prince Stephan the Great triumphs over Hungary and Poland, preservation of the independence of Moldavia
1511 · Moldavia and Walachia become annexed by the Ottoman Empire under limited interior autonomy
1526 · Turks-Battle of Mohács, death of the Hungarian King Ludwig II., the House of Habsburg inherits the Hungarian crown and in this way Siebenburgen/Transylvania
1541 · Siebenburgen/Transylvania becomes dependent from the Ottoman Empire
1593 · Michael the Brave (Mihai Viteazul) becomes Prince of Walachia
1595 · Michael the Brave triumphs over the Turks
1599 · Michael the Brave becomes momentary Prince of Siebenburgen/Transylvania
1600 · Michael the Brave becomes Prince of Moldavia
19th of August 1601 · Michael the Brave becomes murdered, Walachia and Moldavia have to recognize ultimately the Turkish supremacy
1683 · annihilation of the Turks in front of Vienna, march in of imperial-austrian troops in Siebenburgen/Transylvania
1699 · Peace of Karlowitz, the Ottoman Empire recognizes the Roman-German emperor as Prince of Siebenburgen/Transylvania, end of the Turkish control
1711 · the Turks triumph over the Moldavian-Russian liberation armies, the Princes of Walachia and Moldavia become dismissed and substituted by Greek proconsuls (Fanariots)
1716–1718 · Turk's War
21.07.1718 · Peace of Passarowitz (Pozarevac), the Ottoman Empire cedes the Banat, the Small Walachia and Northern Serbia to the House of Habsburg
1739 · the Small Walachia and Northern Serbia were handed over back to the Ottoman Empire
since 1774 · increase of the Russian influence
1775 · ceding of the Buchenland (Bukovina - "Beech Tree Land") to Austria
1806–1812 · Russian-Turkish War
1812 · Peace of Bukarest, the eastern part of the Romanian Principality of Moldavia (between the rivers Prut and Dnjestr) come under the name Bessarabia to Russia
1821 · great Anti-Turkish revolt in Walachia under Tudor Vladimirescu, greek national uprising in Greece, the rule of the Fanariots becomes terminated by the Ottoman Empire
1828–1829 · Russian-Turkish War, defeat of Turkey, Russia establishes a kind of a protectorate üver Moldavia and Walachia, but the Turkish supremacy consist furtherly
1848–1849 · civil-democratic revolution in Moldavia, Siebenburgen/Transylvania and Walachia, the Prince of Walachia resigns momentarily, the revolution in Moldavia and Walachia becomes suppressed by Turkish and Russian troops, the Siebenburgen/Transylvania revolution aims against Hungary
4th of March 1849 · new Austrian imperial constitution, Siebenburgen/Transylvania becomes a crown land of the Austrian monarchy with an own parliament
1856/58 · Crimean War, Treaties of Paris, the Russian protectorate becomes substituted by a protectorate of seven European states, Moldavia earns the Northern Dobruja
1859 · Colonel Alexandru Ioan Cuza becomes elected to the Prince of Walachia and Moldavia
1861 · Prince Ioan Cuza proclaims the Principality of Romania by unification of Walachia and Moldavia
1866 · Prince Ioan Cuza of Romania becomes unseated by a conspiracy, Carl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1839–1914) becomes new Prince of Romania (Carol I.)
17th of February 1867 · the parliament of Siebenburgen/Transylvania passes with its Hungarian majority the connection to the Hungarian monarchy, Siebenburgen/Transylvania becomes an Hungarian province and the parliament becomes dissolved
1877/78 · Russian-Turkish War, Romania is engaged at Russias side in this war, triumph over the Turks
3rd of March 1878 · Peace of San Stefano (Yesilköy), the Ottoman Empire has to recognize the independence of Romania, Great Bulgaria, Montenegro and Serbia, just as the Russian hegemony at the Balkan
13th of July 1878 · Berlin Congress, partial reverse of the Peace of San Stefano as disadvantage for Russia, push aside of the Russian influence at the Balkan, dissolution of Great Bulgaria, recognition of the independence of Romania, (Small)-Bulgaria, Montenegro and Serbia, Romania earns the Dobruja but has to cede the Northern Dobruja to Russia
1881 · Romania becomes proclaimed to a kingdom
1912 · First Balkan War, Serbia, Bulgaria, Greece and Montenegro against the Turkey, Romania remains neutrally, push aside of the Turkey
1913 · Second Balkan War, Serbia, Greece and Romania against Bulgaria, Romania earns from Bulgaria the Southern Dobruja
10th of October 1914 · death of King Carl I., successor is Ferdinand I. of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1865–1927)
1914–1918 · First World War, Romania in engaged in the war since 1916 at the side of the Entente
1917 · bolshevist revolution in Russia, civil war
9th of April 1918 · annexation of Bessarabia by the Kingdom of Romania
1919/1920 · Peace of Saint-Germain and Peace of Trianon, Romania gets Bessarabia officially, the eastern Banat, the Bukovina (Buchenland) and Siebenburgen/Transylvania
1925 · Karl II. resigns and goes in exile
Juni 1927 · Corneliu Zelea Codreanu establishes the "Legion of Archangel Michael" (later "Iron Guard")
20th of July 1927 · death of King Ferdinand I., successor is Michael I. (1921–2017), the son of Carl II.
1930 · Carl II. returns as King of Romania
1937 · great electional triumphs of the "Iron Guard"
1938 · monarchistic-dictatorial rule of King Carl II., struggle against the "Iron Guard", apprehension of Corneliu Zelea Codreanu
30th of November 1938 · Corneliu Zelea Codreanu becomes murdered
1939–1945 · Second World War: 1940 the Soviet Union forces Romania to cede Bessarabia, the southern part of the country becomes separated and annexed by the Soviet Ukraine, the northern part becomes annexed to the Moldavian Autonomous Socialistic Soviet Republic and they proclaimed the Moldavian Socialistic Soviet Republic, King Carl II. goes in exile, Michael I. (son of Carl II.) becomes King of Romania again, but Marshal Ion Antonescu becomes proclaimed to the Leader of the State of Romania, Romania cedes the Southern Dobruja to Bulgaria, 1941: Romania is engaged on the side of the German Empire in the fight against the Soviet Union and is able to occupy Bessarabia again and annexes the area to the Southern Bug River, 1944: Bessarabia becomes occupied and annexed by Soviet troops, 24th of August 1944: Romania leaves the alliance with the German Empire, 25th of August 1944: Romania declares the war to the German Empire
1st of June 1946 · execution of Ion Antonescu
1947 · Peace Treaty of Paris, Romania recognizes the soviet annexation and the subsistence of the Moldavian Socialistic Soviet Republic
30th of December 1947 · abolition of monarchy, King Michael I. resigns, proclamation of the People’s Republic of Romania, Bolshewization
1955 · joining to the Warsaw Pact
23th of July in 1965 · rename of Romania in Socialistic Republic of Romania, Nicolae Ceausescu becomes Secretary General of the Communist Party, Romania detaches itself gradually from the soviet influence and steers now a more national-socialistic course
1967 · Nicolae Ceausescu (1918–1989) becomes Chief of State (Chairman of the Council of the State)
1974 · Nicolae Ceausescu becomes President and Chairman of the Council of the State ("Conducator" → Leader)
1970–1995 · after initial successes arise in the seventies potent economic problems, nearly all the since the 12th century in Romania living 250.000 Germans go back to Germany
1989 · riots, people and armed forces overthrow the regime
25th of December 1989 · Nicolae Ceausescu becomes executed together with his wife after a speedy court proceeding, seizure of power by the "Front for the national Salvation" under Ion Iliescu
1990 · elections, Ion Iliescu becomes president, the country becomes renamed in Republic of Romania, proclamation of the Republic of Gagauzia, civil war
1993 · treaty of association between the European Union and Romania
1996 · elections, Emil Constantinescu becomes president
15th of February 2000 · Romania and European Union start the negotiations of joining
1st of January 2007 · Romania becomes a member of the European Union
5th of December in 2017 · death of Michael I., last king of Romania
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen,
RetroBib Retrobibliothek,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Volker Preuß

The name "Romania" goes logically back to the nation of the "Romanians", which its roots has in the Dako-Romans respectively in the Dako-Romanesques. Former the Romanians were called "Walachians" too – there existed even a Principality of Walachia – but the self-denomination was always "Români".
Source: Die Völker der Erde


Kindly supported by: Jürgen Zens (D)
![]()





























































































































