mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Kingdom of Sweden
- parliamentary monarchy
- own name: Konungariket Sverige
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Regional Flags
– Gotland
– Öland
– Scania
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
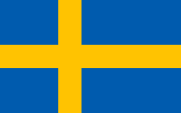
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World





Naval and war flag and naval jack,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Standard of the King,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Standard of the Crown Princes and Princes,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Standard of the King
as Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Standard of a Prince representing the King
as Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Standard of the Minister of Defense,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Standard of the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Standard of the Inspector General of the Army,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World



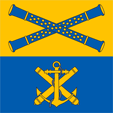
Standard of the Inspector General of the Navy,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World



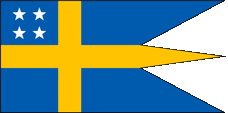
Flag of the Admiral (the King),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



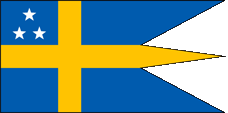
Flag for Vice Admirals,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



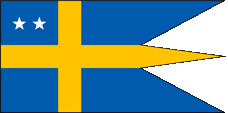
Flag for Rear Admirals,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



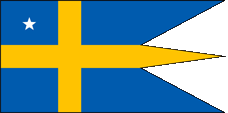
Flag for Commodores,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1396–1523,
Flag of the Kalmar Union (Denmark, Norway, Sweden),
Source, by: Alex Heick




15th cent., Variante,
reconstructed banner of the Swedish kingship,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß



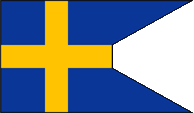
16th cent.–1815, Variante,
Flag of Sweden,
Source, by: Flags of the World



16th cent.–1815, Variante,
Flag of Sweden,
Source, by: Flags of the World



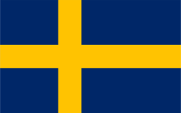
1815–1844, 1905–1906,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World



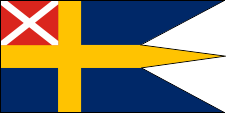
1815–1844,
State, naval and war flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



1815–1844,
Merchant flag in oversea,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



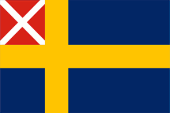
1844–1905,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World



1844–1905,
Naval jack and flag for diplomats,
ratio = 4:5,
Source, by: Flags of the World



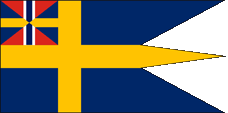
1844–1905,
State, naval and war flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Wikipedia (DE)



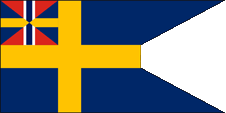
1897–1905,
State flag,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1905–1906,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN)




Pilot flag (pilot call flag),
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World, FOTW
This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is:
 Call for pilot
Call for pilot



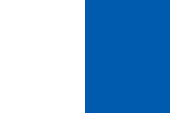
Flag for Pilot Vessels,
Source, by: Flags of the World, FOTW
This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is:
 Pilot on board
Pilot on board




1991,
unofficial flag of Gotland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




Flag of the Region of Gotland,
Source, by: Foto




Flag of the Province of Gotland,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Leonid 2,
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Municipality of Gotland,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Leonid 2,
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons




ca. 1975,
unofficial flag of Öland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (SV)




Flag of the Province of Öland,
Source, by: Wikipedia (SV), Lokal_Profil,
CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons





ca. 1902,
unofficial flag of Scania,
to 1658 a Danish province,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

The today’s flag of Sweden was officially re-introduced on 22nd of June 1906. It shows on blue ground a yellow scandinavian cross (= a cross which is moved towards the pole side [lying cross] – all scandinavian countries use as a sign for relationship and togetherness a lying cross in their flags). The colours have their roots in the very old Three-Crowns-Scutcheon.

About the nascence of the flag exist some theories::
• The Swedish cross flag arised in 1521 under the later King Gustav Wasa in the fights against the enemy Danish. The symbol of the Danish, the "Danebrog" was the model for the Swedish cross flag.
• King Johann III. sayed in 1569 the wish, that the in the great coat of arms of the state used cross, is to take over for all banners and flags in his empire.
• On 6th of June in 1523 Gustav Wasa was crowned to King of Sweden. This day is in Sweden still and until today celebrated as "Flag Day".
• The coronation of Gustav Wasa coincides with the end of the Kalmar Union, whose cross flag could also have been the model.
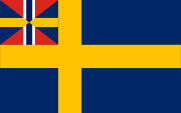
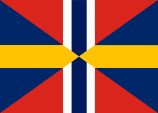
From the 15th century onwards, the central golden cross also played a role on the coat of arms, which King John III. allegedly placed on a simple blue flag in 1569, thus creating today's Swedish flag. With the accession of Gustav I. of the House of Wasa to the throne, the Swedish kingship was re-established in 1523, and the symbolism of Denmark and Norway disappeared from the coat of arms. It is said that it was Gustav I. who created the cross flag, he is said to have used it for the first time during the uprising against the Danes. However, the cross flag seems to be older, with first mentions as early as around 1500. The first official description is found in a royal letter dated on 19th of April in 1562. Even here, it had a swallowtail and seems to have been used by warships at sea. In the early days of Swedish banners and flags, the colours blue and yellow were of course undefined. With the emergence of flags as symbols of a nation in the Napoleonic Era, the present Swedish national flag was created. The flags from this period are reproduced in dark blue, which suggests that the usual indigo was no longer used as a dye, but the Thénards Blue (cobalt blue), which was developed during this period and is based on chemical processes. After the dissolution of the Union with Norway in 1905, the flag of Sweden was used again without a union upper corner for the first time since 1815. In 1906 there was a break, as the shade of blue was newly regulated by the Flag Act of 22nd of June in 1906. The colours were defined as "ljust mellanblå" (light medium blue) and "guldgul" (golden yellow). In the meantime, they have been officially defined by the Natural Colour System as NCS 0580-Y10R for the yellow tone and NCS 4055-R95B for the blue tone. Thus, the following applies to the Pantone mixing system (PMS): pt 301 for blue and pt 116 for yellow. Between 1397 and 1523, the country was part of the Kalmar Union, a Danish-dominated union of the kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden that existed from 1397 to 1523. The Union was never formally fully consummated, but at times it was de facto effective, whenever a Danish king was actually king of all three countries. It was a political idea emanating from Denmark, which was supported outside Denmark only in parts of the nobility and the church. The flag of the Kalmar Union was a cross flag inspired by the Danish danebrog with a red cross on a yellow background. From 1815 to 1906 Sweden was bond with Norway in a personnel union. For that reason in that time the Swedish flag showed (exactly like the Norwegian flag) the so named Union Flag in the upper staff quadrant since 1844.
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


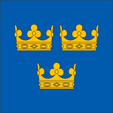
greater Coat of arms of Sweden,
Source: Corel Draw 4

lesser Coat of arms of Sweden,
Source: Corel Draw 4


13th cent.,
Coat of arms of Sweden,
Source: Wikipedia (SV)

14th cent.,
Coat of arms of Sweden,
Source: Wikipedia (SV)

15th cent.,
Coat of arms of Sweden,
without dynastic central shield,
Source: Wikipedia (SV)

15th cent.,
Coat of arms of Sweden,
without dynastic central shield,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

16th cent.,
Coat of arms of Sweden,
without dynastic central shield,
Source: Wikipedia (SV)

The coat of arms of Sweden knows a great and a small implementation. The small coat of arms has its roots in the by King Albrecht about 1364 used seal. It shows shows three golden crowns on blue ground. The three crowns stand for the three regions (historic kingdoms) out of them Sweden was formed: Svealand, Götland and Österland. The great coat of arms shows except the crowns the heraldry of the Folkunger Kings (1250–1364) in squares, divided by a on placed golden cross. The Folkung Dynasty used a golden lion on three diagonal silver bars on a blue background. The bars were executed as wavy lines (streams) from the 16th century onwards. The central shield (heart shield) shows since 1523 the coat of arms of the family of the at any one time reigning kings of Sweden. Nowadays it is twofold divided and shows to the left the heraldry of the between 1523 and 1654 reigning dynasty of the Wasa (golden sheaf on blue-white-red ground) and on the right the heraldry of the family of Bernadotte (golden imperial eagle under the constellation of the Big Bear above of a silvery bridge on blue ground). While the first Swedish king, Waldemar Birgersson, still used the three (Danish?) leopards, a first dynasty established itself with the Folkung around 1250, whose coat of arms showed a golden lion on three diagonal silver bars on a blue background. The bars were executed as wavy lines (streams) from the 16th century onwards. In 1397, Sweden was admitted by Queen Margaret of Denmark to the Kalmar Union, a joint royal union of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. At times, the King of Denmark was thus also King of Norway and Sweden. This was also reflected in the coat of arms, which until the end of the Kalmar Union in 1523 repeatedly showed combinations of the heraldry of the three states, the three blue Danish lions on a golden background, the golden Norwegian lion with the axe on a red background, the Folkung lion, which by now stood for Sweden, even though the Folkung no longer provided the kings. Finally, the three golden crowns on blue, the original Swedish coat of arms, but also welcome as a symbol of the Kalmar Union. From the 15th century onwards, the central golden cross also played a role on the coat of arms. Usually the coat of arms bore an additional heart shield in the middle with the heraldry of the ruling dynasty (e.g. a boat for Bonde, a sheaf of grain for Wasa, etc.).
Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (SV),
Volker Preuß


1927–1937,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

since 1937,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
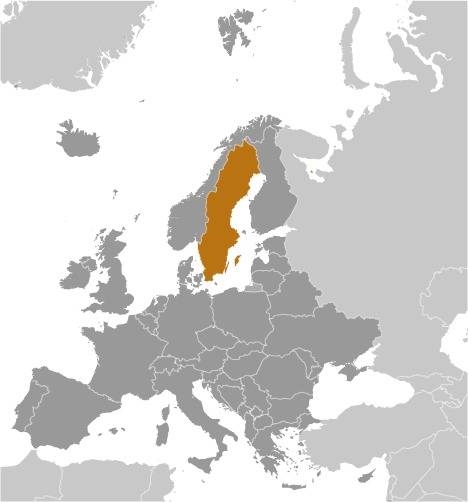
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
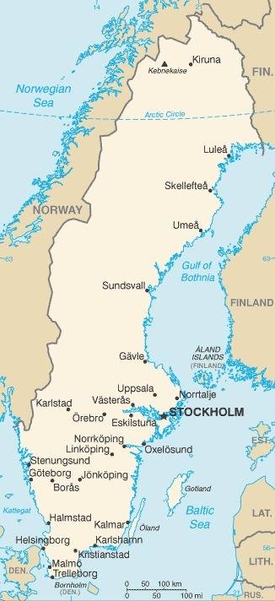
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 172.755 km²
Inhabitants: 10.452.326 (2021), thereof 80,3 % Swedes, 1,9 % Syrians, 1,4 % Iraqis, 1,4 % Finns, 15 % others (Arabs, Poles, Persians, Somalis, Germans, Afghans, Yugoslavs, Turks, Sami)
Religions: 53,9 % Protestant, 4,8 % Muslim, 1,1 % Roman Catholic, 1,1 % Orthodox Christians
Density of Population: 61 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Stockholm, 949.761 inh. (2017)
official Language: Swedish
other Languages: Finnish, Yiddish, Romani, Sami, English, German
Currency: 1 Swedish Crown (SEK, skr) = 100 Öre
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

4th–5th century A.D. · first settlement by teutonic tribes, the Svear (Swedes) and the Gotar/Goetar (Goth/Gauth), establishment od feudal tribal and smaller kingdoms
9th–10th century · the today’s Sweden is the initial position of Viking's journeys, the Swedish Vikings (Normans) were called Waregians, the Waregians invade the habitat of the Eastern Slavians over the rivers Memel (Neman), Western Dvina, Neva and Volchow in the today’s Russia, conquer in 862 the City of Novgorod and establish the Rus of Novgorod, an Norman feudal state, conquer in 882 Kiev and establish the Rus of Kiev, a further Norman feudal state
9th–11th century · christianization by German missionaries, to the Archdiocese of Hamburg-Bremen, since 1104 to the Archdiocese of Lund, since 1164 own Archdiocese of Uppsala (seat of the archbishop)
995–1060 · first (transitional) unification of Sweden under King Olaf Schoßkoenig and his sons, in the afteryears again feudal splintering and throne conflicts, reign of the dynasties of the Ynglingers and of the Stenkyls
12th–13th century · conquest of Finland
1250 · with King Birger Jarl comes the Folkunger-Dynasty on the throne, later creation of a consistent land law, electional monarchy under limitation of the power of the kingship and strengthening of the nobility
1364 · King Magnus from the Folkunger-Dynasty flees from Albrecht III. of Mecklenburg, his son Albrecht becomes elected from thenobility to the Swedish King; the son of Magnus, Håkon VI., becomes King of Norway
1389 · Queen Margarete I. of Denmark triumphs over King Albrecht, he becomes set down
1397 · the grand nephew of Queen Margarete I., Erich VII. of Pommern (Pomerania), becomes crowned in Kalmar to the King of Denmark, Norway and Sweden (Kalmar Union)
1434 · central-swedish farmer revolt against King Erich under Engelbrecht Engelbrechtsson
1436 · struggle of the Swedish Marshal Karl Knutsson against King Erich
1439 · King Erich resigns
1448 · Karl Knutsson becomes elected to the Swedish King, long lasting conflicts of Schwedens against Denmark-Norway
1470 · death of King Karl Knutsson, continuation of the fight against Denmark-Norway under Sten Sture the Older and Sten Sture the Younger
1520 · victory of the Danish over the troops of Sten Sture the Younger, Stockholm Carnage
1523 · accession to the throne by Gustav I. from the Wasa-Dynasty, ultimate separation from the Kalmar Union with Denmark-Norway
1527 · Reichstag (Parliament) of Västerås: expropriation of the church, introduction of reformation
1544 · introduction of the herital monarchy in Sweden
1560–1569 · times of the rule of Erich XIV. from the Wasa-Dynasty, cautious policy of expansion to get back the swedish western coast from Denmark and influx in the trading with Russia
1561 · conquest of Estonia
1563–1570 · First Nordic War, Denmark, Poland and Lübeck against Sweden
1570 · Peace of Stettin after the First Nordic War, maintain of the status quo
1592–1604 · times of the rule of Sigismund III. (1587–1632 even King of Poland), failed attempt of the counter-reformation
1604 · King Sigismund III. from the Wasa-Dynasty becomes dismissed by the Swedish Reichstag
1604 · accession to the throne of Karl IX. from the Wasa-Dynasty
1611–1632 · times of the rule of King Gustav II. Adolf, Sweden becomes a great power
1610 · conquest of Ingermanland
1617 · conquest of Karelia
1629 · conquest of Livonia
1630 · Sweden is engaged in the since 1618 raging German Thirty Years War against the catholic emperor
1632 · Gustav II. Adolf, King of Sweden from the Wasa-Dynasty becomes killed in a battle of Luetzen (near the town of Leipzig), successor as Queen of Sweden is his daughter Christine
1638 · foundation of the north american colony of New Sweden in the today’s Delaware (federal state of the USA)
1645 · Sweden acquires the west coast province of Halland and Oesel Island from Denmark, as well as the provinces of Jaemtland and Herjedalen from Norway
1648 · Westfalian Peace after the German Thirty Years War, Sweden acquires Fore Pommerania, Wismar Town and the Dioceses of Bremen and Verden
1652–1657 · Swedish colony of Witzen (Takoradi) at the Guinea Coast in Africa
1652–1659 · Swedish colony of Cape Coast at the Guinea Coast in Africa
1654 · Queen Christine renounces for the throne in favour of her cousin Karl X. Gustav, end of the dynasty of the Wasa
1654–1660 · times of the rule of King Karl X. Gustav from the house of Zweibruecken
1655 · Sweden cedes New Sweden to the Netherlands
1655–1657 · Second Nordic War, war between Sweden, Poland, Russia, Denmark, Brandenburg and the Emperor of the German Empire
1657–1659 · Swedish colony of Fort Wilhelm at the Guinea Coast in Africa
1657–1659 · Swedish colony of Christiansborg (Accra) at the Guinea Coast in Africa
1658 · Peace of Roskilde with Denmark, Denmark cedes the west coast provinces of Bohuslän, Blekinge and Schonen, as well as the province of Trondheim in Norway and Bornholm Island to Schweden
1660 · Peace of Oliva after the Second Nordic War, re-make of the status quo of 1655
1660 · Peace of Kopenhagen with Denmark after the Second Nordic War, Sweden has to sede back Bornholm and Tronheim to Denmark
1660–1697 · times of the rule of King Karl XI., consolidation of the power in the innards of the empire
1697–1718 · times of the rule of King Karl XII.
1700–1721 · Third Nordic War (THE Nordic War), Denmark, Saxony, Poland, Russia, Prussia and Hanover against Sweden
1719, 1720, 1721 · Peaces of Stockholm, Frederiksborg and Nystad after the Third Nordic War, Sweden has to cede the dioceses of Bremen and Verden to Hannover, Sweden has to cede Southern Fore Pommerania to Prussia, Sweden has to cede Livland, Estonia, Dagoe Island, Oesel Island, Ingermanland and Karelia to Russia, companionway of Sweden as great power and ruler of the Baltic Sea
1721–1772 · „times of freedom“, period of time with broad civil rights, granted by Reichstag (Parliament) and Reichsrat (Empires Counsel)
1771–1792 · times of the rule of King Gustav III. from the house of Zweibruecken
1772 · King Gustav III. enforces the introduction of a new constitution, restriction of the rights of the Reichsrat, reconstruction of absolutism
1789 · King Gustav III. enforces in the Reichstag the introduction of the „File of unification and security“ and unites in his person nearly unlimited power
1792–1809 · times of the rule of King Gustav IV. Adolf from the house of Zweibruecken
1803 · Sweden pledges Wismar Town to the Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, in 1903 it becomes handet over to Mecklenburg-Schwerin
1809 · Russia conquers Finland, Sweden has to cede even the Åland Islands to Russia after the Peace of Fredrickshamn, King Gustav IV. Adolf becomes unseated
1809–1818 · times of the rule of King Karl XIII. from the house of Zweibruecken
1810 · King Karl XIII. adopts the by the Reichstag to the successor of the throne determined French Marshal Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte (crown prince Karl Johann), they hope in this doing for French support against Russia
1813–1815 · Sweden is engaged in the Liberation Wars against Napoléon, in the Peace of Kiel in the year 1814 Denmark has to cede Norway to Sweden, Norway becomes united with Sweden in personnel union (the King of Sweden is at the same time the King of Norway)
1815 · Vienna Congress, reconfiguration of Europe after the era Napoléon, Sweden has to cede Fore Pommerania (Stralsund Town) to Prussia
1818–1844 · times of the rule of Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte as King Karl XIV. Johann, establishment of the until today existing royal Swedish dynasty of the Bernadotte, in the afteryears waxing politics of neutrality, in the domestic politics gradually liberal reforms
1848 · liberal cabinet
1905 · Norway terminates the union with Sweden and becomes fully sovereign
1914–1918 · First World War, Sweden stands neutrally
1918 · constitutional reform: common suffrage
1920 · joining in the League of Nations
1939–1945 · Second World War, Sweden stands neutrally, ca. 300 Swedes fight voluntary on the side of the German Empire
1946 · joining to the UNO
1949 · founder member of the European Council
1951 · founder member of the EFTA
1953 · joining to the Nordic Council
1971 · constitutional reform
1975 · new constitution, the king has none political power anymore
1978 · the succession in the monarchy becomes switched to the right of the first-born
1986 · assassination of the social-democratic premier Oluf Palme
1994 · plebiscite for the joining to the European Union
1995 · joining to the European Union
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
RetroBib Retrobibliothek,
Avantgarde für Europa

In the Swedish name of the country "Sverige" are to perceive the words "Svear" and "Riket", Sverige = Svear-Riket = "Empire of the Svear".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen



![]()

















































































































