mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- parliamentary monarchy with the British monarch as chief of state
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen






Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen




1962–2022,
Flag of the Queen,
ratio = 4:7,
Source, by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen





1655–1660,
Flag of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen



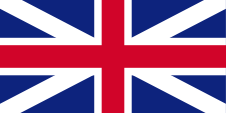
1660–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1801–1875,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1875–1906,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




1906–1957,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




1957–1962,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)



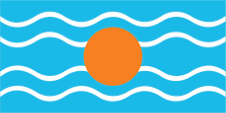
1958–1961,
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1962,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




1957–1962,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




The today's flag was hoisted up for the first time on the 6th of August in 1962 on the occasion of the independence of the country. The flag is divided by a yellow (golden) diagonal cross into two green and two black triangular fields. The green stands for the hope and the agriculture, the yellow (gold) for the sunlight and the natural resources (minerals), and the black for the difficulties of the past, but in the presence, too. The colours of the flag were fixed in a before organized competition. Initially Jamaica was a British Colony. The flag was in that times a so called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack pointed out to the connections to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. The badge of 1875 showed the today's blazon as oval with the helmet and the crocodile above. Since 1906 the coat of arms was showed in the Blue Ensign – the official flag of the colony – within the white disc. Apart from black, the colors of the flag of Jamaica are defined as follows: yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355. If the flags follow British specifications, the following also apply here: blue = Pantone 280, red = Pantone 186.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Flags of the World


Coat of arms of Jamaica,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms was alredy awarded to the then British colony in the year 1661. It shows in silver (white) a red cross (Cross of St. George), added by five golden (yellow) pineapple fruits. Upon the shield an helmet, and upon the helmet a crocodile on a stem. As shield holders serve an arawak indian couple, which stands on a banner with inscription. Since 1906 the coat of arms was showed even in the Blue Ensign – the official flag of the colony – within a white disc. Previously (since 1875) there appeared only a badge. That showed the blazon as oval with the helmet and the crocodile above. In the year 1957 the coat of arms gots few changed, as the helmet was styled some abundanter and the banner with inscription was creased otherwise. In the year 1962, the year of independence, was the hitherto used motto in the banner with inscription "Indus uterque serviet uni" (Both India will serve one") changed into "Out of many, one People". Furthermore the colour of the banner was changed from silver to gold.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
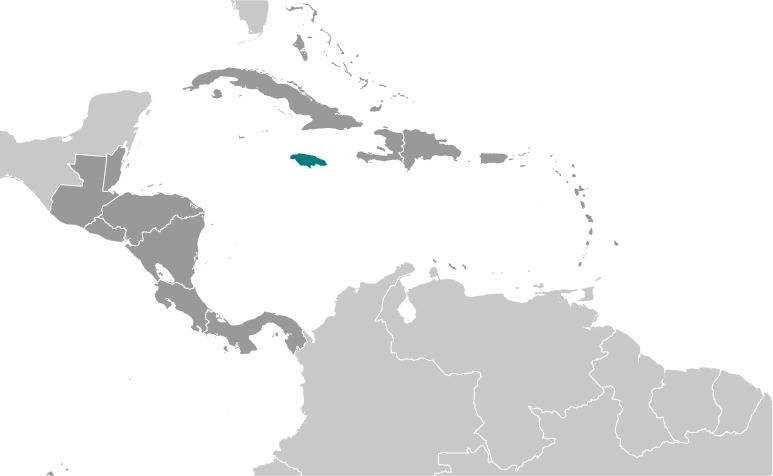
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
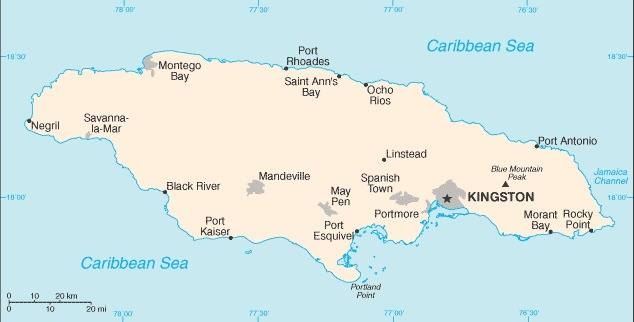
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 4.244 square miles
Inhabitants: 3.000.000 (2020), thereof 92,1% of African descent, 6,1% Mulattos, 0,8% Asian, 0,2% Europeans (including 500 Germans) and Chinese
Religions: 53% Protestant, 4% Roman Catholic, 3% Anglican, 1% Rastafari
Density of Population: 707 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Kingston, 648.683 inh. (2010)
official Language: English
other Languages: Creole English
Currency: 1 Jamaica Dollar (JMD, J$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 5 h
Source:
1. Wikipedia (DE),
2. Wikipedia (EN),
"Hilfe für Deutsche im Osten Europas. Warum?", Bundesministerium des Inneren, 1992

1494 · discovered by Columbus
1510 · colonization by Spain
1536 · formal Spanish colony in ownership of the descendants of the Columbus, the dukes of Veragua, eradication of the Indian natives
1655 · British conquest, build up to the center of the British possessions in West India
1795 · big slave uprising
1834 · abolition of the slavery
1866 · crown colony
1940 · the USA lease on Jamica military bases for the time of the war
1943 · general suffrage
1944 · new constitution
1953 · United Kingdom grants limited self administration
1st of January in 1958 · formation of the West Indian Federation (confederation of nearly all British possessions in the Caribic)
1961 · granting of expanded self administration
19th of September in 1961 · successful plebiscite for the leave of the West Indian Federation (in 1962 dissolved)
6th of August in 1962 · independence in the frame of Commonwealth of Nations
1972–1980 · phase of democratic socialism, economic decline
1983 · Jamaica takes part in the US-american invasion of Grenada
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Wikipedia (DE)

The name of the country goes back to the language of the Caribbean, the extincted Indian population. "Chaymaka" was in the language of the Caribbean "the well watered". Other sources cite the Arawak Indians as a source. In their language is "xaymaca" to translate as "land of water sources". On which people the name its roots actually has, can not be determined beyond doubt. Both peoples lived on the island at the same time.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Wikipedia (D),
Atlas der wahren Namen


![]()











































