mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of India
- parliamentary federal republic
- own name: Bhárat Ganráshtra
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Historical Flags
· British East India Company
· British India
· Portuguese India
· French India
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Free India – Azad Hind
• Regionale Flaggen
· Jammu and Kashmir
· Sikkim
• Sezessionen
· Nagaland
· Assam
· Khalistan
· Mizoram

National flag and naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






Merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen




State ensign (official flag at sea),
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Merchant flag for Naval Reserve Officers
and flag of auxiliary ships,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 2022,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Indian Navy, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3 (1:2 ?),
Source, by: Flags of the World




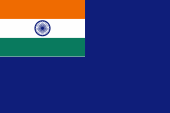
The today's flag of India was introduced on 22nd of July in 1947 in advance of the independence on the 15th of August in 1947. It shows three horizontal stripes in saffron, white and green. Into the white middle stripe was placed a blue wheel. This is the religious symbol "wheel of tutorage". It goes back to the emperor Ashoka which united and ruled India between 270 and 232 B.C. It became to a buddhistic symbol, because Buddha's first near Benares pronounced sermon was named "turning on the wheel of tutorage" (Chakra). The colour saffron stands officially for courage and sacrifice, white for peace and trust, green for loyalty and chivalry. Unofficial stands the saffron for the hindus the green for the muslims and the white for the forgiving spirit between them. The flag of India has it's roots in the flag of the Indian National Congress from 1931, and goes back to Subhas Chandra Bose (1897–1945, look here). In context with the independence was displaced the in the blue middle stripe positioned blue spin wheel (Charkha) by the Chakra. The prince's states – which all had their own flags – were ultimately abolished in 1950. They got substituted by factitiously created federal states which use no own flags except one exception (former Jammu and Kashmir). India is orientated in the British Ensign-System. This points to the former connexions to United Kingdom (→ British India). The colors of the flag are defined as follows: Saffron Yellow = Pantone 021, Green = Pantone 341, Navy Blue = Pantone 662.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (DE)

India:
1950–1971,
Flag of the president,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen




1950–2001,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




2001–2004,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




2004–2014,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




2014–2022,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




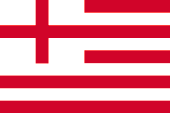
ca. 1615–1707,
Flag of English East India Company,
Source, by:
commons.wikimedia.org



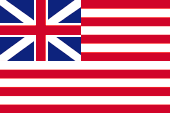
1707–1801,
Flag of British East India Company,
Source, by:
commons.wikimedia.org



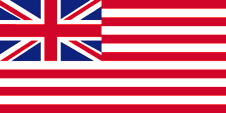
1801–1858,
Flag of British East India Company,
Source, by:
commons.wikimedia.org



The flags of the East India Company showed since the beginning of the 17th century white and red stripes, to differentiate better its ships from the other British ships.
mehr Informationen? → click or tap here


1879–1947,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1945–1947, unofficial,
Merchant flag,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1879–1928,
Naval flag,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



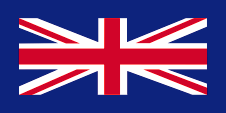
1879–1928,
Naval jack,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



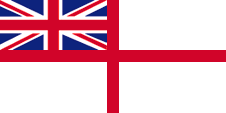
1928–1947,
Naval flag,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1928–1947,
Naval jack,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



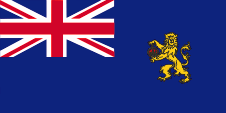
1884–1947, Local Maritime Government Ensign,
Official flag at sea,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1885–1947,
Flag of the Vice King and Governor General of British India,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. The symbol of British India was the Star of India, a silvery five-pointed star surrounded by a blue ribbon with the motto: "The Light of Heaven our Guide ", embedded in golden sun rays. The conquest of India by United Kingdom was appreciably finished until the year 1856, in 1858 the British took officially over the throne of the Mogul-Empire, and in the year 1877 the British queen Victoria adoped the title „Empress of India“. India was now a patchwork carpet from territories administered by the British East Indian Company, respectively directly by United Kingdom, and territories of indigenous princes which merely recognized the British supremacy (vassals). All this territories maintained their own native heraldry partially completed by British symbolism, for instance by introduction of a Red Ensign, or introduction of a Blue Ensign. The prince's states were ultimately abolished in 1950. They got substituted by factitiously created federal states which use no own flags except one exception (Jammu and Kashmir).
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (DE)


1830–1910,
National flag of Portugal,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Brasil Imperial




1911–1961,
National flag of Portugal,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4






Sixties of the 19th cent.,
purposed flag for Portuguese India,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)




1935–1961,
Flag of the Governor General,
Source, by:
Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



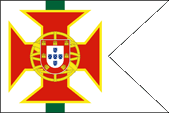
1935–1961,
Flag of a District Commandant
in Portuguese India,
Source, by:
Flaggenbuch 1939



Between the 16th and 18th centuries, Portugal operated numerous urban possessions and bases on the eastern and western coast of India and in Ceylon. In the 19th century there were still five of them left on the western coast: the in 1535 acquired Diu, the in 1559 acquired Daman, the in 1779 acquired Dadra, the in 1779 acquired Nagar-Haveli and the largest estate, the in 1509 acquired Goa. Dadra and Nagar-Haveli were lost in 1954 by an occupation by Indian nationalists. They are now a union territory of India. Goa, Diu and Daman were in 1961 occupied by the Indian army and became abandoned against the command of the Portuguese President. Diu and Daman are today a union territory of India and Goa, with its 1429 sq.mi., is the smallest Indian federal state. In the Portugese colonies was solely in use the Portugese national flag because they saw the colonies as permanent component of the motherland and not as outer possessions. This implys that Portugese colonies never had own flags, even if there were ambitions in the sixties of the 20th century to introduce flags for the colonies by placing of the coat of arms of the colony in the flying end of the Portugese national flag. But this plans became never realized.
Source:
1) Wikipedia (D),
2) Wikipedia (D)

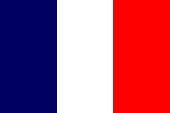
1794–1954,
National flag of France,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4





In the middle of the 18th century, the French influence, based on extensive possessions on the eastern coast, had grown considerably. After the "Seven Years War" (1756 to 1763) – lost by France – these possessions were almost entirely transferred to the United Kingdom. Only five cities remained as French possessions: the in 1751 acquired Yanam (Yanaon), the in 1738 acquired Karikal (Karaikal), the in 1674 acquired Pondichéry (Puducherry), the in 1721 acquired Mahé and the in 1673 by Frenchman founded Chandannagar (Chandernagor). Chandannagar was handed over to India in 1950 after a referendum. The remaining four possessions came to France in 1954 and they are now a union territory of India.e never realized. In the French colonies was solely in use the French national flag because they saw the colonies as permanent component of the motherland and not as outer possessions. That implys that these colonies never had own flags.
Source:
FOTW,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (D)


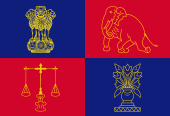
Coat of arms of India,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

Badge of British India,
Source, by:
Flags of the World

Coat of arms of Portuguese India,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

The coat of arms of India was adoped on 26th of January in 1950 in occasion with the passing of a new constitution. The Indian flags do not show the coat of arms, merely and is not to see on the indian flags, merely the flag of the president uses it in the left upper canton. It is reproduced by a column in the holy town Sarnath and shows a plinth with emperor Ashokas wheel in the middle, thereupon four lions which look in the four directions. Underneath a quotation in Sanskrit out of the Mundaka Upanishades: "only the truth wins".
The symbol of British India was the Star of India, a silvery five-pointed star surrounded by a blue ribbon with the motto: "The Light of Heaven our Guide ", embedded in golden sun rays.
In the year 1935 own coats of arms were created for the Portuguese colonies. The design was subject to a special scheme. So each coat of arms contained, in addition to a local symbolism, the five Quinas from the coat of arms of Portugal and five green waves on silver. As the local symbolism in the coat of arms of Portuguese India appeared a red castle and a steering wheel.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D)


1947–1950,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

since 1950,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
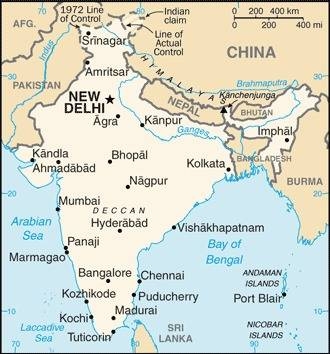
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 1.269.214 square miles
Inhabitants: 1.380.004.000 (2020), thereof 72% Indo Aryans, 25% Drawida, 2% Mongoloid
Religions: 80% Hindus, 14% Muslims, 2% Christians, 2% Sikhs, 1% Buddhists
Density of Population: 1.087 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Neu-Delhi, 250 000 inh. (2011)
official Languages: Hindi, English
other Languages: Urdu, Bengali, ... 22 regional languages are officially approved, too.
Currency: 1 Indian Rupee (INR, iR) = 100 Paise
Time Zone: GMT + 5,5 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

ca. 2500 B.C. · neolithic before-aryan high cultures of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa
ca. 1500–500 B.C. · immigration of Aryan nomad nations to North and Northwest India (Wedyan Age)
ca. 640 B.C. · beginning expansion of the Buddhism
320–185 B.C. · Maurja Empire
270–232 B.C. · regency of the Maurja king Ashoka
320–467 A.D. · Gupta Empire
since ca. 660 · penetration of the Islam
since 1221 · repeated Mongolian invasions
1498 · the Portugese Vasco da Gama achieves India over the sea
1503–1559 · appropriation of diverse Indian coastal towns by the Portugese, among them – even for the next 400 years – the towns Goa, Diu and Daman
1526 · foundation of the Mongolian emperor's dynasty (Mughal) of the Babur in Dehli
1600 · establishment and privilegement of the English East India Company
1602 · establishment of the Dutch East India Company
1605–1663 · appropriation of further Indian coastal towns by the Dutch
1611 · the Dutch cede Mastsjulipattinam to the English East India Company, beginning of the British colonization, initially as well only by subjugation of diverse coastal towns
1620 · appropriation of Trankebar by Denmark, in 1845 ceded to the English East India Company
1664 · establishment of the French East India Company
1674–1739 · appropriation of further Indian coastal towns by the Frenchmen
18th cent. · ascent of the Marathe's Empire in South India, gradual decay of the Mogul Empire
1753 · capture of one first greater tract of land (Sarkars coastal region) by the British East India Company
1765–1898 · the British (incl. the British East India Company) submit step by step the whole India including the today's states Pakistan, Bangladesh and Burma
1778 · four islands of the Nicobar Islands are declared as Austrian crown colonies, despite of Danish claims, and the "Triestinian East India Trade Company" was founded
1784 · the Nicobar Islands become abandoned by Austria, the "Trieste East India Trade Company" ends their work
1813 · the privileges in trade of the British East India Company become terminated
1814 · the Netherlands cede their remaining possessions to the British
1833 · the activities of the British East India Company become limited to the exertion of the civil government in the name of the crown
1846 · the Nikobare Islands become a Danish possession, in 1869 ceded to United Kingdom
1858 · United Kingdom takes officially over the throne of the Mughal Empire, India becomes a British colony, the British East India Company becomes insignificant (dissolved in 1873)
1877 · the British queen Victoria adopes the title „Empress of India“
1885 · foundation of the Indian National Congress (congress party)
1906 · foundation of the Moslem League
1919 · formation of a first own government for British India
1935 · constitutional reform, granting of partial internal self administration, the provinces get autonomy
1937 · Burma gets separated from British India and receives internal self administration
1943–1945 · Subhas Chandra Bose tries to achieve independence for whole India during the Second World War with the Indian National Army as an ally of Japan and Germany
15th of August 1947 · because of religious agitations partition of British India into India (Hindus) and Pakistan (Muslim), independence for both states as dominions within the British Commonwealth
1947–1949 · first Kashmir War against Pakistan
26th of January 1950 · India becomes republic, remains however in the Commonwealth
1954 · France cedes it's possessions in India (Chandannagar - already in 1950, Pondichéry, Yanam, Mahé and Karikal)
1961 · Portugal gives up it's possessions in India (Goa, Diu and Daman)
1962 · frontier war against China
1965 · second Kashmir War against Pakistan
1971 · war against Pakistan to support the separation of Bangladesh from Pakistan
1984 · war againsts the Sikh separatists which fight for an independent Sikh State of Khalistan
1987 · invasion of Indian troops in Sri Lanka
1990 · withdrawal of the Indian troops from Sri Lanka
1992–1993 · quarrels between Hindu and Muslim
1999 · armed campaigns between India and Pakistan in Kashmir
2019 · abolition of the federal state of "Jammu and Kashmir", division into the union territories of "Jammu and Kashmir" and "Ladakh"
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte

The name of the country goes back to different languages. In Sanskrit, the land is called "Sindh", what means "land by the river" and refers to the Indus River. In Urdu is the name of the country "Hind". In Hindi, the country is called "Bharat", what means "Union". Bharat is the official name of the country.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen

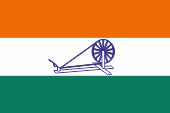
since 1931,
Flag of the Indian National Congress,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Constitution of the INC, 2010




1943–1945, Azad Hind,
Flag of the Provisional Government of the Free India,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
more Info: Azad Hind ← click here




1943–1945, Azad Hind,
Flag of the Indian National Army,
more Info: Azad Hind ← click here





1957–2019,
State flag,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)



Jammu and Kashmir (more precisely, the Indian part of Kashmir) was the one and only Indian federal state which officially used an own flag. On 5th of August in 2019, the Government of India decided to abolish the special status for the federal state and to divide it into the two Union Territories namend


1967–1975,
Staats- und Maharadschaflagge,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)



Sikkim was once a British and after 1947 an Indian protectorate, and was in 1974 incorporated as a federal state by India.
more informations? → click or tap here

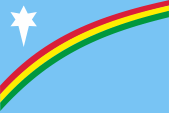
Flag of Nagaland,
Source, by:
UNPO



Nagaland tryed to deprive itself from the growing Indian influence since 1954 and was regardless incorporated to India as a federal state in the year 1962. Thereafter armed resistance under that flag.
more informations? → click or tap here


Flag of Assam,
Source, by:
Stateless Nations



Assam came in 1816 under the supervision of the Kingdom of Burma and became British in 1826. From 1905 till 1924 Assam belonged to the Bengalen Province and was levied to a province in 1924. In the year 1947 Assam got shared between India and (East)Pakistan – the today's Bangladesh. The Indian spare part was levied to an Indian federal state. Because of separatist agitations was the Mizo Hills District detached from Assam in the year 1972 and administered directly from New Delhi. Since the eighties of the 20th century there are separatist ambitions in Assam too, under the above flag.


Flag of Khalistan,
Source, by:
Stateless Nations



Since the conquest of the Sikh State by the British in the year 1849 there were ever again ambitions of the Sikhs to resist the central control. In 1947 the Sikh Province Punjab was even shared between India and Pakistan what some contributed to the further destabilization in the region. In the year 1984 there were already outspoken fightings between the Sikhs and Indian troops, and in the course of them was raid the central sanctuary of the Sikhs, the Golden Temple in the town Amritsar by the Indian troops. The Sikhs aim for an own state under the above flag which should carry the name Khalistan.

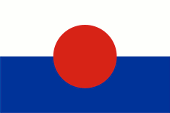
Flag of Mizoram,
Source, by:
Stateless Nations



Because of separatist agitation of the Chin people was separated the District of Mizo Hills from the Indian federal state Assam in the year 1972, and administered directly from New Delhi. At the end of the eighties of the 20th century Mizoram got levied to a federal state, however they failed to dam in the separatist ambitions. In opposite the insurgent Chin in Mizoram fused with the Chin in Burma and aim for a mutual own state under the above flag.
more informations? → click or tap here


![]()

























































































































