mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Kingdom of Norway
- parliamentary monarchy
- own name: Kongeriket Norge
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Exterior properties:
- Spitsbergen (Svalbard)
- Bear Island
- Jan Mayen
- Bouvet Island
- Peter I Island
- Norwegian Antarctic Territorry
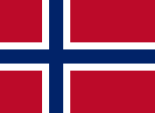
since 1898,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 8:11,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4





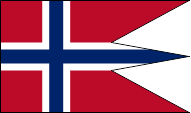
since 1905,
State and naval flag,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen




Naval jack,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Royal flag,
ratio = 5:7,
Source, by: Flags of the World



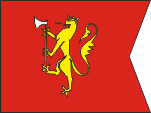
Flag of the Crown`s Prince,
ratio = 5:7,
Source, by: Flags of the World



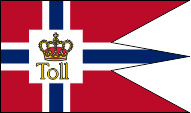
Customs flag,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



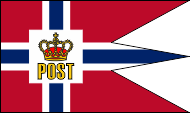
Postal flag,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Differentiational flag for official pilot's vessels,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Differentiational flag for private pilot's vessels,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



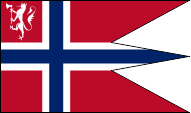
Flag the of Minister of Defense,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



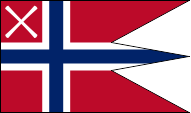
Flag of the Commanding Admiral (Grand Admiral),
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



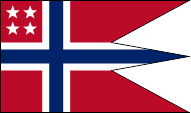
Flag for Admirals,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flags of the World



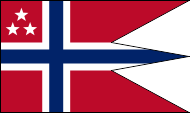
Flag for Vice Admirals,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flags of the World



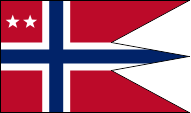
Flag for Rear Admirals,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flags of the World



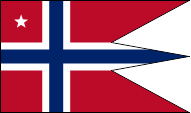
Flag for Commodores,
ratio = 16:27,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1396–1523,
Flag of the Kalmar Union (Denmark, Norway, Sweden),
Source, by: Alex Heick



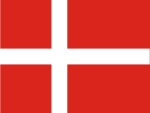
17th cent. to 1814,
Flag of Danmark-Norway,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4





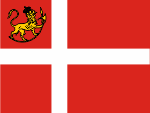
1814–1821,
National flag and merchant flag in coastal waters,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)



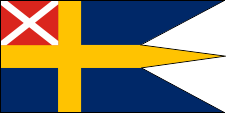
1815–1844,
State and naval flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)



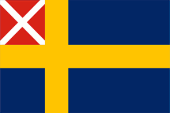
1818–1844,
Merchant flag in overseas,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)





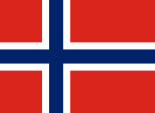
1821–1844,
Merchant flag in the North Sea,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4





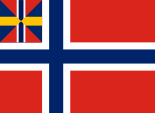
1844–1899,
National flag and merchant flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)



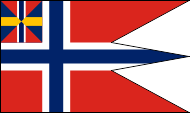
1844–1905,
State and naval flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)



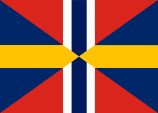
1844–1905,
Naval jack,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




since 1899,
National and merchant flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)






1914–2002,
Flag of the Chief of Coastal Artillery,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Meaning/Origin of the Flag
The flag of Norway – introduced on 17th of July in 1821 – is red with a blue white-bordered Scandinavian Cross, what means a cross which is to the pole-site. All Scandinavian countries use as a sign for relationship and togetherness such a cross in their flags. Between 1397 and 1523, the country was part of the Kalmar Union, a Danish-dominated union of the kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden that existed from 1397 to 1523. The Union was never formally fully consummated, but at times it was de facto effective, whenever a Danish king was actually king of all three countries. It was a political idea emanating from Denmark, which was supported outside Denmark only in parts of the nobility and the church. The flag of the Kalmar Union was a cross flag inspired by the Danish danebrog with a red cross on a yellow background. The Norwegian cross has its root in the ambitions for independence in the 19th century. In this way the flag was created by placing of a blue cross onto the white cross of the Danish "Danebrog". The colours blue, white and red should consciously remember the French Tricolor. The today’s flag of Norway was introduced on 17th of July in 1821 officially only to use ashore. The restriction for using at sea was abolished on 10th of Decmeber in 1898. The colours of the flag are prescribed by law as "deep red" and "dark blue", but without specifying them further. Thus, different colour specifications can still be found today. However, the following colours have become widely accepted: blue as Pantone 281 and red as Pantone 200. Of course, these are modern standards, which in the past, based on vegetable dyes, may have led to different colour results.
In the May of the year 1814 – still in the times of the union with Denmark – the Danish flag was added by a lion with an axe (the Norwegian scutcheon symbol since 1280) in the upper staff quadrant to create a Norwegian flag. After the end of the union with Denmark in the August of 1814 it was allowed to use this flag still until 1821, but only ashore and in coastal waters. Otherwise – quasi as merchant flagg – there was to use the Swedish flag with a red upper staff quadrant with a white diagonal cross in it. On 17th of July in 1821 (by other sources on 16th of May in 1821) was adoped the today’s Norwegian flag, but it was allowed to use it only ashore and in coastal waters too. In 1844 was created a "Unions Upper Staff Quadrant" for the Norwegian and Swedish flags. That combined by a diagonal quartering the Swedish and Norwegian cross. The Swedish and Norwegian flags showed therewith each the "Unions Upper Staff Quadrant" and express in this way the personal union between the monarchies of both countries. On the 11th of October in 1899 (by other sources on the 10th of December in 1898) was it allowed to use the Norwegian national and merchant flag without the "Unions Upper Staff Quadrant". After the declaration of independence of Norway on the 7th of June in 1905 was finally left out the "Unions Upper Staff Quadrant" even on the naval flag. Further but only momentary changes, e.g. in the naval flag, were done under the Quisling Government (1940–1945).
Source:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Coat of arms of Norway,
Source: Corel Draw 4

Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
The coat of arms shows on a red shield a golden and crowned lion with an axe. The lion, since 1217 the device of Norway (coat of arms of King Haakonsson), was added about 1280 by the axe (emblem of King Olaf). The necklace of his order surrounds the shield on the royal coat of arms.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen

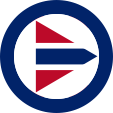
since 1945,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1914–1940,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
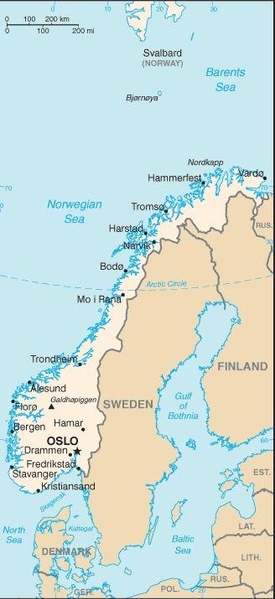
Source: CIA World Factbook

Numbers and Facts
Area: 148.729 square miles
Inhabitants: 5.425.270 (2022), thereof 81% Norwegians, 8,9% Europäer Europeans (Jews, Forest Finns, Roma, Swedes, Finns, Germans), 9,6% other (Asians, Africans, Latin Americans), 0,8% Sami
Religions: 65% Protestant, 3,8% other Christian, 3% Roman Catholic, 3,1% Muslim, ca. 19% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 37 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Oslo (1624–1924 called Kristiania), 699.827 inh. (2022)
official Language: Norwegian = Riksmål (Bokmål) = Danish variation of Norwegian dialects
other Languages: Norwegian = Landsmål (Nynorsk) = in 1853 created factitious language made from diverse Norwegian dialects
Currency: 1 Norwegian Crown (NOK, nkr) = 100 Øre
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (DA),
CIA World Factbook

antiquity · settlement by Germanic tribes
ca. 700–1100 · raids of seafaring Norwegians (named Vikings)
872 · tribal King Harald Hårfagr beats the other tribal kings and unifys the empire momentary
995–1000 · momentary unification of the empire, settlement of the Faroe Islands, thereafter comes Norway to Denmark
1000 · the Norwegian (Viking) Leif Eriksson discovers Greenland and Northern America
1028–1035 · reign of the Danish King Knud the Great
1174–1263 · civil war
1261 · Danish-Norwegian conquest of Greenland, annexion to Norway
1262 · Danish-Norwegian conquest of Iceland, annexion to Norway
1319–1360 · personal union with Sweden, introduction of the Norwegian Law
1380 · Olaf, son of the Swedish King Haakon VI. Magnusson and of the Danish Queen Margarete becomes King of Norway and Denmark, onset of the personal union of Denmark-Norway
1397 · Kalmar Union, Margarete I. of Denmark-Norway binds Sweden to the crown too
1523 · disintegration of the Kalmar Union, Sweden separates from Denmark-Norway, the Danish kings remain as kings of Norway
1687 · the Danish Law becomes transfered to Norway, Norway loses in this way its relative independence and becomes quasi a Danish province
1709–1721 · Great Nordic War
1750 · first demands for an own school system, for a National Bank and financial independence
1801 · King Frederick VI. of Denmark, takes Napoléon's part, the First Consul of France
1807 · annihilation of the Danish fleet by the British
14th of January 1814 · Peace of Kiel, Danmark has to cede Norway (without Greenland, Iceland and the Faroe Islands) to Sweden, rejection by the Norwegians
17th of May 1814 · the Norwegian nation's assembly (Storting) passes an own Norwegian constitution with the Danish Prince Christian Frederick as king
14th of August 1814 · resignation of King Christian Frederick because of Swedish pressure, the Storting decides for independence of Norway under personal union with Sweden → the Swedish King Charles XIV. becomes King of Norway too, installation of a Swedish proconsul
1848 · arising of liberal and democratic movements
1873 · abolition of the Swedish proconsul
1884 · constitution, constitutional monarchy
1905 · the parliament (Storting) declares the personal union with Sweden for terminated, election of the Danish Prince Charles to the King Haakon VII.
1914–1918 · First World War, Norway remains neutrally, but gives its fleet under the order of United Kingdom
9th of April 1940 · (Second World War) Norway becomes occupied by German troops, establishment of an exile government in London, arise of a resistance movement, formation of a national socialistic government in Norway, 8.000 Norwegians fight voluntary on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union
1942 · Vidkun Quisling becomes premier
October 1944 · Northern Norway becomes occupied by soviet troops
8th of May 1945 · capitulation of the German troops, re-democratization
24th of October 1945 · execution of Vidkun Quisling
1949 · joining of Norway to the NATO
1994 · rejection of the joining to the European Union by a plebiscite
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Avantgarde für Europa

The name "Norway" means the "northern ways" which were once gone probably at the settlement of the country.
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen



![]()


















































































