mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- also: Cook Archipelago
- with New Zealand associated state, de facto possession of New Zealand
- own names: Rarotonga: Kuki Airani, English: Cook Islands
- other names: Mangaia Archipelago, Hervey Islands
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
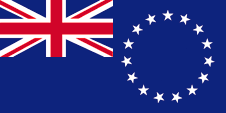
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Customs flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Representative of British Crown,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World





1893–1901,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



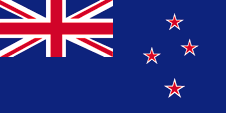
1901–1973,
National flag of New Zealand,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4





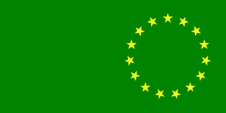
1973–1979,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




to 2012,
Customs flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




As New Zealand stays bound in the ensign-system, the Cook Islands (awith New Zealand associated state) have a Blue Ensign, too, but not until 4th of January in 1979. The former flag, introduced in 1973, was only green with the ring from fifteen stars, and was changed on 4th of january 1979, in context with a change of government. The national flag of the Cook Islands is so a so named "Blue Ensign". This is a dark blue flag cloth with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper staff quadrant. The Union Jack points to the former colonial connexions of the islands to United Kingdom. The United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" => civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment => the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. The Cook Islands, since 1965 with their own government, do not use a badge in this meaning, but a circle from fifteen white stars, which represent the islands of the archipelago.
The island of Rarotonga had introduced its own flag in 1850, a flag in the colors red and white, as usual in Polynesia. It showed three horizontal stripes in red, white and red, with three blue stars in the middle of the white stripe. After the establishment of the British Protectorate, the Union Jack was placed in the upper corner. In 1893, two years after the formation of the Federation, a badge with a palm tree in the middle of the Union Jack was inserted, and the flag became officially adopted for the Cook Islands Federation. From the year 1901, when the islands came to New Zealand finally, here was only to use the flag of New Zealand, to the 23rd of July in 1973, as a first own flag was adopted. It was single-coloured green, and showed in the flying end a ring of 15 golden stars. Each of these stars stood for one of the islands of the country. After a political change of power was introduced the today's flag on 4th of January in 1979.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D)


Coat of arms of the Cook Islands,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

The Coat of Arms of the Cook Islands has a shield as its focal point The shield contains the fifteen stars found on the national flag. A flying fish (maroro) and a White Tern (kakaia) are on each side of the shield, one supporting a cross as a symbol for Christianity, the other holding a Rarotongan club (momore taringavaru) as a symbol for the richness of Cook Islands' tradition. Orators used to hold it during traditional discourses. The helmet is an ariki head-dress (pare kura) of red feather, symbolising the importance of the traditional rank system. The name of the nation is on a banner below the shield. The coat of arms was designed by Papa Motu Kora, a mataiapo, a traditional chiefly title from the village of Matavera in Rarotonga. Papa Motu is the secretary of the House of Ariki -- the house of paramount chiefs from all over the Cook Islands. He has held this post for many years and is well known in the Cook Islands as a tumu korero or traditional orator.
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
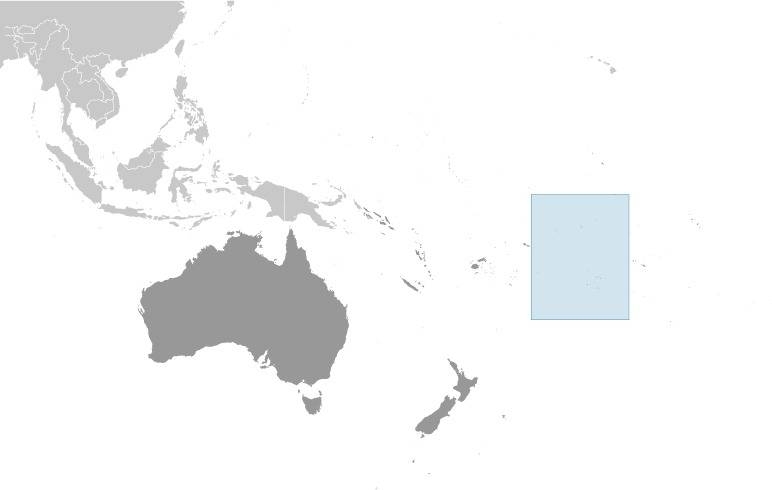
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
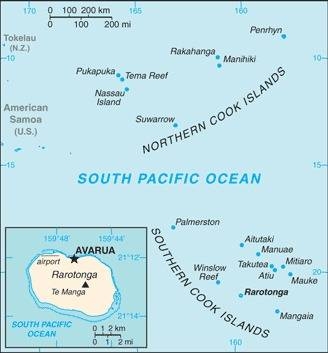
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 93 square miles, — consisting of a northern archipelago with the islands of Manihiki, Nassau, Penrhyn (Tongareva), Pukapuka (Danger), Rakahanga and Suwarrow, and a southern group, the Manihiki Islands or Roggeveen archipelago, with the islands/island groups of Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Atiu, Mangaia, Manuae , Mauke, Mitiaro, Palmerston (Pamati) and Takutea.
Inhabitants: 18.600 (2011), thereof 93% Cook Islands Maori
Religions: 55% Protestant, 17% Roman Catholic
Density of Population: 199 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Avarua (on Rarotonga), 13.095 inh. (2011)
official Languages: English, Rarotonga
other Languages: lokal languages of the islands: Pukapuka, Penrhyn, Rakahanga, Manihiki
Currencies: 1 New Zealand Dollar (NZ$) = 100 Cents, 1 Cook Islands Dollar (NZ$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 10 h
Besonderheit: The Cook Islands, although an Associated State, are not fully sovereign. They are not a member of the UN, there is no own citizenship (all the residents are New Zealanders), but the islands are curiously recognized as independent from two dozen states until today, including the FRG since 2001.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuss,
Länder der Erde

9th century · colonization by Polynesians
20th of October in 1595 · the Spanish seafarer Alvaro de Mendana de Neyra lands on the island of Pukapuka, and thus he discoveres the today's Cook Islands
1606 · the in Spanish orders traveling seafarer Pedro Fernández de Quirós lands on Rakahanga
1722 · the Dutch seafarer Jacob Roggeveen comes the southern archipelago during his circumnavigation of the Earth
1764 · British sailors reach Pukapuka and name it Danger Island
1773–1779 · The British seafarer James Cook discoveres Manuae Island on 23rd of Sept. in 1773, and reaches several times the Roggeveen Archipelago
1789 · the British seafarer William Bligh lands on Aitutaki
1813 · start of the colonization by United Kingdom, from New Zealand and Australia
1877 · the islands become part of the British Western Pacific Territories (to 1901)
26th of October in 1888 · the islands become officially a British protectorate
5th of June 1891 · establish of the Cook Islands Federation
7th of October in 1900 · the islands become subordinated under the administration of New Zealand
11th of June in 1901 · the islands become annexed to New Zealand
4th of August in 1965 · New Zealand grants self-government in association with New Zealand under recognition of the British monarch as head of state, New Zealand takes over foreign policy and defense
1991 · friendship treaty with France about trade, economic and military protection
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

When the British navigator James Cook on 23rd of September in 1773 discovered Manuae Island, he gave it the name "Sandwich Island", in honor of John Montagu, the 4th Earl of Sandwich. Cook in 1778 changed the name in Hervey Iceland, in honor of the First Lord of the Admiralty, and the name Sandwich Islands becomes transfered to Hawaii. Meanwhile it became clear that Manuae Island has many neighboring islands (the Roggeveen Archipelago), and Cook summarized all the Islands in the region under the name of "Hervey Islands". The Russian seafarer Admiral Adam Johann of Krusenstern, who made between 1803 and 1806 a world circumnavigation, renamed the Hervey Islands to "Cook Islands" in honor the famous British navigator. In 1824 he noted this name in his maps – Krusenstern was now head of the cadets corps and honorary member of the Academy of Science. This has prevailed.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuss


![]()



























