mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- possession of Great Britain
- own name: The Bermuda Colony
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1999,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D),
Flags of the World,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons






since 1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




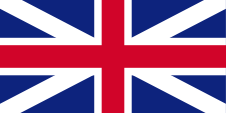
1660–1801,
Flag of the United Kingdom (to 1707 of England),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen






1801–1875,
Flag of the United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen





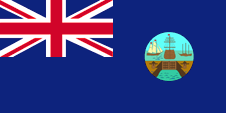
1875–1910,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



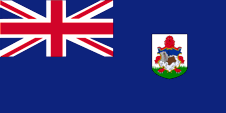
1910–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




1915(?)–1967,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




1915(?)–1967,
Unofficial national flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




1967–1999,
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




The Union Jack points to the connexion to Great Britain. On the Bermuda Islands, only the flag of the United Kingdom was initially used, what changed in the middle of the 19th century, because, the United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" => civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the government => the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission had been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. This was allowed to the Bermudas since 1910, following orther souces since 1915. In this way an own merchant flag with the badge of the colony was created. Additionally private persons quickly and to a considerable extent startet to use the actual merchant flag on land instead of the British Union Jack, more or less as the national flag. The government was aware of this practice, but no action was taken against it. Finally, the use of the Red Ensign with the badge as the national flag was allowed in 1967.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other. The Badge was introduced in 1875 and showed three sailing ships at anchor, and one of them is waiting outside a closed port gate. According to other sources, is that a dock. The today's coat of arms was introduced in 1910.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Flags of the World


since 1910,
Coat of arms of the Bermuda Islands,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
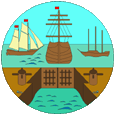
1875–1910,
Badge of the Bermuda Islands,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The Coat of Arms of the Bermudas – awarded on 4th of October in 1910, shows a bear, holding a shield with an allegorical scene: A sinking ship in front of cliffs. The ship is the "Sea Venture". She foundered in 1609 and left behind the first involuntary residents on the islands for two years. The golden banner below the coat of arms shows the motto "QUO FATA FERUNT" => "Where fate drives us". The Badge was introduced in 1875 and showed three sailing ships at anchor, and one of them is waiting outside a closed port gate. According to other sources, is that a dock.
Source: Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (DE)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
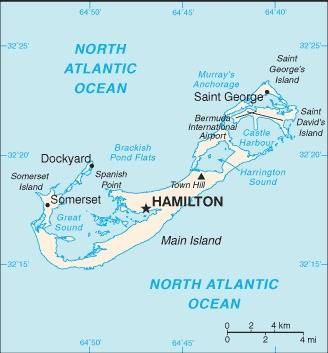
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 20 square miles
Inhabitants: 63.779 (2016), hereof 54% of African origin, 31% Europeans
Religions: 45% Protestant Christians (thereof 30% Anglican), 15% Catholics
Density of Population: 3.117 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Hamilton, 854 inh. (2016)
official Language: English
Currency: 1 Bermuda Dollar (BMD, BD$, B$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1503 · The Spanish navigator Juan de Bermúdez suffers nearly shipwreck at the coast and discoveres in this way the islands
1609 · The "Sea Venture", a ship from England on his way to Virginia, suffers shipwreck off the coast
from 1612 · colonization by the British Virginia Company, and later by the Bermuda Company, Headquarters: Saint George
1684 · crown colony with its own governor
1790 · foundation of Hamilton
1815 · Hamilton becomes capital
1941 · construction of naval bases (USA, Canada, United Kingdom)
8th of June 1968 · autonomy
1995 · closure of the naval bases
15th of August 1995 · a referendum decides against independence
Source: Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen,
Länder der Erde

The Bermuda Islands are named after the Spanish navigator Juan de Bermudez who in 1503 off the coast nearly suffered shipwreck, and discovered the islands in this way. A settlement was not done. In 1609, suffered the "Sea Venture" – a ship from England on the way to Virginia – shipwreck off the coast, and the castaways, who escaped to land, named the islands after their leader: Somers Islands. Although the islands were colonized from 1612 by Britain, the name retained as Bermudas. This name appeared on maps for the first time in the year 1511.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()






































