
Merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Naval jack ,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 1988,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




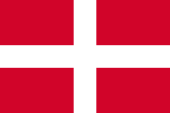
1530–1798,
Flag of Malta (Order of Malta),
Source, by: World Statesmen



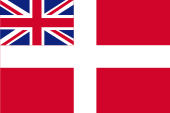
1814–1864,
unofficial merchant flag,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1875–ca.1898,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




ca.1898–1923,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1921–1943,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
uncertain,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Flaggenbuch 1939




ca.1898–1943,
unofficial national and merchant flag,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1923–1943,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1943–1964,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1943–1964,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



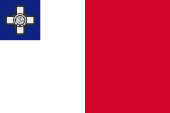
1943–1954,
unofficial national and merchant flag,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1954–1964,
National and merchant flag,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1967–1974,
Flag of the Queen,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1964–1974,
Flag of the Gouvernor General,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The flag of Malta is vertically white and red striped with a red-bordered Cross of St. George in the upper staff quadrant. It was officially hoisted in this shape for the first time on the occasion of the achievement of independence on 21st of September in 1964. The colours white and red have their roots in the Norman's Count Roger II. (1095–1154), which conquers the island in the year 1090 and liberated it from the Muslims. The colors white and red have always been present on the island and were probably used as the unofficial national and trade flag from 1898 onwards. In the times of the British colony was in use – but not until 1875 – the British official flag, so a Blue Ensign with the badge of the islands in the flying end of the flag. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. From 1921 it was said that a Red Ensign could also be used. It is not possible to provide proof of this. The badge was a white-red shield in party per pale on a white disk. In the year 1943 Malta was awarded by King George IV. the Cross of St. George as praise for the bravery of the Maltese during the bombardments in the Second World War. This distinction was added in a blue upper canten on the shield of the badge. The unofficial white and red flag was then also supplemented by the blue upper corner with the St. George's Cross and was used in this way from 28th of December in 1943. In 1954 this flag is said to have been officially approved. As Malta became independent on 21st of September in 1964 was removed the blue upper canton and the Cross of St. George was added by a red border to distinguish it better. There are versions of the flag with a filled Cross of St. George in blue, pale blue or silvery (pale gray) or there is renounced for the representation of the minutiaes (the Holy George kills the dragon) in the interior of the cross. The merchant flag of Malta has its roots in the insignias of the Christian Order of St. John (also Maltesian Order), which ruled the islands between 1530 and 1798. That shape of the cross in the flag is from there also named Maltesian Cross. Between 1964 and 1974 Malta belonged not only to the British Commonwealth of Nations but was even not a republic. Chief of State was the British Queen. In hers function as Maltese Chief of State she had an own flag.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


since 1988,
Coat of arms of Malta,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

1975–1988
Coat of arms of Malta,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen

The today's coat of arms remembers the in 1964 introduced coat of arms. That showed the white-red (silvery-red) shield with a blue upper canton and in it the Cross of St. George (→ look above among "flag"). Above a golden helmet with white-red covers and a golden wall-crown. As shield supporters served two dolphins. Below the shield arised the Maltesian Cross as well as the motto of the state. After Malta became republic in 1974, they thought they have to introduce a new coat of arms. In this way was adoped a seal as new coat of arms on 11th of July in 1975, which showed a coastal scene with the rising sun, a fishing boat, a shovel and a pitchfork. Underneath the new name of the state: "Republikka Ta'Malta". After a change of government the coat of arms was changed again on 19th of October in 1988 (by other sources on 28th of October in 1988). In its until today valid form it shows again the white-red shield with a silvery, with a red bordered Cross of St. George in the left upper canton. Above the shield a golden wall-crown and to the left and to the right of the shield a green olive twig (left) and a green palm tree twig (right). Both are tied together with a white ribbon which carrys as inscription the name of the state: "Republikka Ta'Malta".
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Flaggen und Wappen,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1980–1988,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
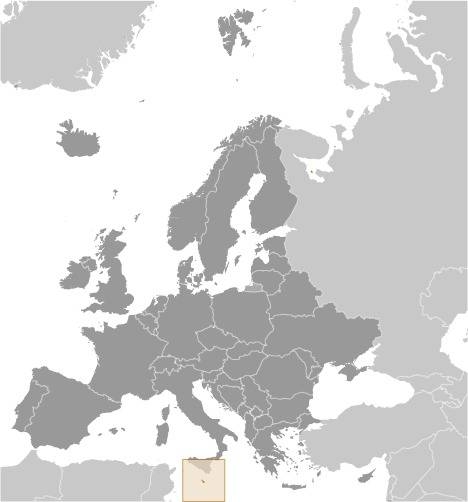
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
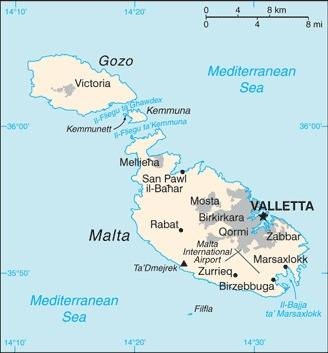
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 122 square miles
Inhabitants: 519.562 (2021), thereof 98% Maltese, 2% other Europeans (British, Germans)
Religions: 94% Roman Catholic, 4,5% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 4.258 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: La Valetta, 5.827 inh. (2018)
official Languages: Maltese, English
other Languages: Italian
Currency: 1 Euro (€) = 100 Cent
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

14th – 7th cent. B.C. · phoenician settlement
7th cent. B.C. · to the Empire of Karthago
218 B.C. · as "Melita" to the Roman Empire
395 A.D. · at the partition of the Roman Empire Malta comes to the West Roman Empire
533 · to the East Roman Empire (Byzantium)
870 · conquest by Arabs, Islamization
1090 · conquest by the Normans (Count Roger of Normandy), to the Kingdom of Sicily, re-christianization
1530 · the Christian Order of St. John gets Malta as fiefdom from Emperor Charles V.
1798 · conquest by troops of Napoléons
1800 · liberation of the islands by British troops and troops of the Kingdom of Naples
1814 · Vienna Congress, Malta comes to United Kingdom, becomes a British crown colony
14th of April 1921 · constitution, limited autonomy
1940–1943 · Second World War, extensive bombardments
1947 · internal autonomy
21st of Sept. 1964 · independence (within the framework of the British Commonwealth of Nations)
13th of December 1974 · Malta becomes a republic but remains in the Commonwealth
1965 · joining to the European Council
1979 · the last British troops leave the country
2004 · joining to the European Union (EU)
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The name "Malta" has its roots in the Latin "Melita", and that word should be real older because it comes from the Indo-Aryan word "mel", what means "high".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()

























![]()
