• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Suvadiva Republic

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






alleged naval flag,
uncertain,
ratio = 2:3,
Source: Flags of the World




since 1968,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source: Flags of the World





19th century,
National flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1903–1926,
National flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1926–1953,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Flaggenbuch 1939



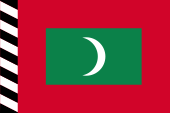
1926–1953,
State flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN), Flaggenbuch 1939




1926–1953(?),
Merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939



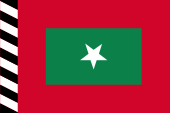
1926–1953(?),
Offshore state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939



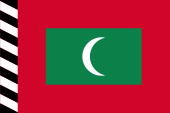
1953–1965,
National and state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1954–1965,
Flag of the Sultan,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1965–1968,
Flag of the Sultan,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)



1958–1963, Secession
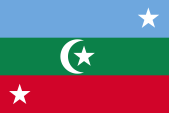
Flag of the Suvadive Republic,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




The national and merchant flag of the Maldives shows a red bordered green field with a white crescent. It was officially hoisted in its today's design on 25th of July in 1965 for the first time. Today, the following meanings are interpreted into the colours of the flag: Red stands for the blood of the nation's heroes and their willingness to sacrifice every drop of blood to defend their country. Green stands for peace and prosperity and the moon for Islam, which is the state religion in the Maldives. The colours of the flag are indicated as follows: Red = Pantone 186, Green = Pantone 348. The original flag of the islands was a single-coloured red cloth how it was wide spread as national flag in many countries around the Indian Ocean. Even under the British protectorate was this flag continued. At the beginning of the 20th century, a 13-way diagonal black and white stripe began to be added to the flag at the mast. It was called "Dhandimathi". The black and white stripes stood for the 13 archipelagos the Maldives consist off. Between 1926 and 1932, the white crescent was then added to the centre of the flag, however, the two ends of the crescent pointed towards the flagpole. Amir Abdul Majid Didi, who was the country's prime minister between 1926 and 1932, initiated a major change on the flag during his tenure: he had added the green field to the centre of the country's flags. The Maldives was administered as a British colony from Ceylon (now Sri Lanka). When Ceylon became independent in 1949, the Maldives remained under British administration and a republican constitution was adopted in 1953. This was also reflected in the state flag – which could now also be used as the national flag – because the moon was rotated, with the two ends of the crescent pointing towards the waving end of the flag. The Sultan was reinstated in 1954, the flags remained unchanged. The Maldives became independent from Great Britain in 1965, on this occasion the black and white Dhandimathi stripe was removed from all flags. Red is in the region of the Indian Ocean a flag color with a great tradition and wide dissemination, from the coasts of Arabia, over Zansibar to the Maldives, which stands in dense context to the islam. Red flags had and have all islamic dynasties, which come from the Alawites (Alides, descentants of Ali) like today Morokko or former North Yemen, the Arabian Emirates and Oman. Oman incorporated till 1730 the african eastern coast, to an in the today Mocambique. They moved their capital to Zansibar (ca. 1830) and founded a new empire which had its red flag, too.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild,
Volker Preuß,
Wikipedia (EN)


Coat of arms of the Maldives,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of the Maldives shows a crescent with star in front of a palm tree between two national flags. Below a banner with the Arabic inscription »AI-Daulat al Mahldibiah«. The palm tree symbolizes the nature of the country, the crescent and the star the Islamic state's religion. The coat of arms was last changed in the 1990s, when the crescent and star were changed from silver to gold.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Wikipedia (DE)

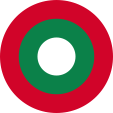
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
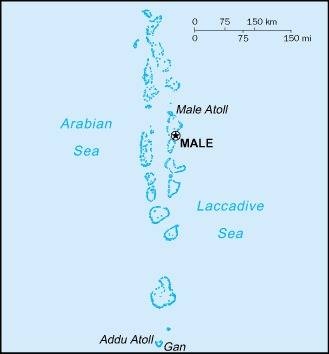
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 115 square miles
Inhabitants: 541.000 (2020)
Religions: Sunni Islam as state religion, other religions are forbidden
Density of Population: 4.700 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Malé, 153.904 inh. (2014)
official Language: Diwehi (Meledivian)
other Languages: Arabic, English
Currency: 1 Rufiyaa (MVR, Rf) = 100 Laari
Time Zone: GMT + 5 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

2nd cent. · settlement by Singhalese from India
12th cent. · immigration of Arabs and Persians → beginning islamization
1153 · the Islam becomes state's religion
ca. 1150 · foundation of the sultanate
1512 · discovery by Portugese seafarers
1518 · Portugese attempt of conquest, the King of Candy (Ceylon) assumes the protectorate over the country
1558 · conquest by Portugal
1573 · the Portugese leave the islands
1645 · establishment of Netherlands protectorate out of Netherlands Ceylon
1796 · by the establishment of the British rule on Ceylon the Maledives come formally from the Netherlands to United Kingdom
1887 · establishment of the British protectorate
1932 · first constitution
1948 · because of the independence of Ceylon results the administrative separation from Ceylon
1952 · internal autonomy
1953 · proclamation of the republic
1954 · reinstatement of the Sultan
1959–1963 · Separatist secession of the "Suvadive Republic" on the three southern atolls of the Maldives
1960 · establishment of a British Air Force base on Gan Island
26th of July 1965 · independence, the Maldives become a member of the Commonwealth of Nations
11th of November 1968 · abolition of the sultanate and proclamation of the republic
1975 · withdrawal of the British troops from Gan Island
1988 · attempted coup d'état by Tamil mercenaries
1989 · withdrawal of the in 1988 into the country beged Indian troops
2003 · Mass demonstrations, riots
2004 · state of emergency
2012 · Mass demonstrations, riots
2016 · the Maldives leave the Commonwealth of Nations
2020 · the Maldives rejoin the Commonwealth of Nations
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
World Statesmen

The logos "Maldives" is probably formed by europeization of the name "AI-Daulat al Mahldibiah". That Arabic words mean in translation: "State of the Islands in front of the Malabar Coast". But the official self-denomination of the country is "Divehi Rajje" → "Maledivian Republic".
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()




















![]()
