mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Guinea-Bissau
- authoritarian presidial republic with multi-party-system
- own name: Repúblika da Guiné-Bissau
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4







1911–1973,
National flag of Portugal,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4






sixties of the 19th cent.,
purposed flag for Portuguese Guinea,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)




to 1935,
Flag of a High Commissioner,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggenbuch 1939



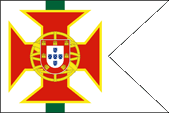
1935–1961,
Flag of a District Commandant,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flaggenbuch 1939




1935–1973,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




The today's flag of Guinea-Bissau was inroduced on the 24th of september in 1973 in context with the declaration of independence. It shows two horizontal stripes in yellow and green and near the pole a vertical stripe in red, thereupon a black five-jagged star. These star is the symbol for Africa and it's black population, he is directly derived from the flag of Ghana. This flag corresponds (except the lacking initials) to the in the year 1961 introduced flag of the PAIGC-party. The colour red stands for the in the fight for freedom given blood, yellow stands for the sun and the natural resources of the country, green stands for the vegetation and the agriculture. The colors are defined as follows: red = Pantone 032, yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355. The combination of the colours green, yellow and red in the today's flag are the Pan-African colours: Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. For the political unity of Africa stands the colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african countries in their flags after the independence. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. In the times of the Portugese colony was solely in use the Portugese national flag because they saw the colonies as permanent component of the motherland and not as outer possessions. This implys that Portugese colonies never had own flags, even if there were ambitions in the sixties of the 20th century to introduce flags for the colonies by placing of the coat of arms of the colony in the flying end of the Portugese national flag. But this plans became never realized.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Flags of the World


since 1973,
Coat of arms of Guinea-Bissau,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

1935–1974,
Coat of arms of Portuguese Guinea,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)

The coat of arms of Guinea-Bissau was - like the flag - introduced in the year 1973. It shows the pan-african colours and even the on the flag shown black star. In the below part of the coat of arms is to see a golden conch. It stands for the Cape Verde Islands. On a red saying-ribbon between two green palm-tree twigs (they stand for the mainland) the motto of the state: "Unidade, Luta, Progresso" → "Unity, Fight, Progress". In the year 1935 own coats of arms were created for the Portuguese colonies. The design was subject to a special scheme. So each coat of arms contained, in addition to a local symbolism, the five Quinas from the coat of arms of Portugal and five green waves on silver. As the local symbolism in the coat of arms of Portuguese Guinea appeared a black field with the golden scepter of King Alfonso V.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
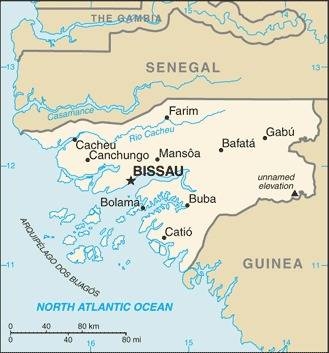
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 13.948 square miles
Inhabitants: 1.970.000 (2020), thereof 28% Fulbe, 22% Balanta, 14% Mandingo (Malinke), 9% Pepel, 8% Mandyak (Manjaco)
Religions: 85% Muslim, 8% Christians, 7% Animist, 2% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 141 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: (São Joé des) Bissau, 407 000 inh. (2007)
official Language: Portuguese
other Languages: Balante, Fulani, Malinke, Creole Portugese (Crioulo)
Currency: CFA-Franc BCEAO (FCFA, XOF) = 100 Centimes, FCFA = Franc Communauté Financière d'Afrique, to 1997: 1 Guinea Peso (PG) = 100 Centavos
Time Zone: GMT
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1446 · the Portuguese Nuño Tristão discovers and explores the coast of the today's Guinea-Bissau
1460 · foundation of the Portuguese merchant base Cacheu
1630 · Portugal claims territories and dominates the trade on the coast
1687 · foundation of the first Portuguese settlement near the today's Bissau
1765 · foundation of the town São Joé des Bissau
1792 · British settlement trial near Bolama fails
1879 · foundation of the Portuguese Guinea Colony
1884 · United Kingdom and France establish merchant stations on the coast
1885 · Berlin Conference: Portuguese Guinea gets adjudged to Portugal
1941 · transfer of the capital from Bolama to Bissau
1951 · Portuguese Guinea becomes an overseas province
1955 · granting of partial inner autonomy
1956 · foundation of the leftist extremistic liberation movement "Partido Africano da Independencia de Guinea-Bissao e Cabo Verde" (PAIGC)
1963 · start of the armed fight of the PAIGC against Portugal
24th of September in 1973 · the PAIGC declares unilaterally the independence of Guinea-Bissau, Luis Cabral (PAIGC) becomes president
25th of April in 1974 · revolt of the Portugese army against the government of Caetano in Portugal
10th of September in 1974 · Portugal recognizes the independence of Guinea-Bissau
1980 · racial motivated coup d'état by Major J. B. Vieira, Cabral gets unseated
1981 · organizational separation of the PAIGC, on the Cape Verde Islands arises the PAICV
1984 · new constitution, Vieira gets confirmed as president, the since the foundation of the state intended unification with the Cape Verde Islands becomes excluded for the future
1990 · initial stages of democratization
1991 · introduction of the multi-party-system
1994 · elections for parliament and president, absolute majority for the PAIGC, Vieira gets confirmed as president
1998 · army revolt, civil war
2010 · military coup attempt
2012 · military coup
2014 · elections, unstable power relations in the following years
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Weltgeschichte,
Discovery '97

The name "Guinea" goes back to the Berber word "aguinaou", what means "blacks" and referred originally to all residents of the West African coast from Senegal to Gabon. The second part of the country's name, "Bissau", helps to distinguish between other states which bear the name "Guinea" and refers to the capital of the country. In the time as a Portuguese colony, the country was called Portuguese Guinea.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Volker Preuß


![]()















