
click here → Tamil Eelam

The current Sri Lankan flag was officially introduced on 22nd of May in 1972 and changed slightly in the corners of the reddish brown field on 7th of September in 1978. It shows a large reddish brown field on the right side within a yellow frame, and on the left – in a smaller field – two vertical stripes in green and saffron yellow. A yellow sword-bearing lion can be seen within the dark red field, and yellow leaves of the Bo tree in the corners. The large right field corresponds to the flag of the old Sinhalese Kingdom of Kandy (kingdom of Udarata) with the royal emblem of the golden lion. Yellow is the colour of Buddhism. The yellow frame around the flag symbolises the protection of the country by this religion. The green stripe symbolises the country's Muslim minority, and the saffron-yellow stripe represents the Hindu minority of the Tamils. The colours of the flag are defined and laid down in a document of the Sri Lanka Standards Institution (SLSI), probably from 2020, including in the colour space RGB, yellow 247-183-24, reddish brown 148-30-50, orange 223-117-0 and green 0-95-86, which would correspond approximately to the following Pantone colour numbers: yellow = 1235 C, reddish brown = 194 C, orange = 716 C and green = 3292 C. Before this color definition, the colors of the flag were reproduced quite arbitrarily, so that in practice, as flags, on websites or in specialist literature, they were always reproduced quite differently. Every now and then there are said to have been official regulations, for example in 1978, when the brown field was said to have been changed to reddish brown.
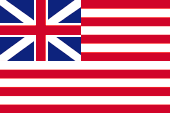
Sri Lanka is based on the British Ensign system. This points to the previous connections to Great Britain. Ceylon became a British crown colony in 1802, the flag of Great Britain was raised, the country became part of the United Kingdom, received its own administration and its own governor. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the United Kingdom through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag".
In 1864, United Kingdom introduced a flag system in which:
• Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner.
From 1865, ships of colonial governments were allowed to fly a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. The badge of Ceylon was a blue disc with a red border, decorated with gold. On the disc was a scene with an elephant in front of a Buddhist pagoda.
Sri Lanka became independent on 4th of February in 1948, but remained in the British Commonwealth of Nations, with the British monarch as head of state, and the first flag of independent Ceylon was introduced. It corresponded to the flag of the old Kingdom of Kandy, which had resisted the Europeans to the last. The non-Buddhist (Muslims) and non-Sinhalese (Tamils) population did not accept this flag. It was therefore changed to its present form on 2nd of March in 1951 by adding a green and saffron-yellow stripe. On 22nd of May in 1972 Ceylon became a republic, some flags in the British tradition were changed or abolished. For example, the St. George's Cross was removed from the naval flag in 1972. The Blue Ensign as the state flag and the Red Ensign as the merchant flag were abolished – although probably not immediately – along with some other changes to other flags. One detail of the national flag was also changed: The roof tips of a pagoda (according to other sources "old Ceylonese poles"), which had previously been shown in the four corners of the reddish brown field, were replaced by leaves of the Bo tree. The Bo(dhi) tree (also Pipul Tree or Pippala Tree) is the tree under which Buddha received enlightenment. However, there is some uncertainty as to whether the Blue Ensign (state flag) and the Red Ensign (merchant flag) have actually been abolished. There is no binding information on this. Many sources at least still cite the red merchant flag. Despite all its emancipation, Sri Lanka's current flags are still orientated on the British ensign system. In connection with the adoption of a new constitution, the shape of the Bo leaves was changed slightly in 1978. Each President of Sri Lanka has his own personalised flag, which is individually designed.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Wikipedia (DE),
World Statesmen,
Volker Preuß


1875–1948,
Emblem (Badge) of British Ceylon,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939

since 1972,
Coat of arms of Sri Lanka,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

The today’s coat of arms of Sri Lanka was adopted in 1972. Until then, a similar emblem was used, from 1948. The coat of arms shows a golden-rimmed, reddish brown disc with the sword-bearing lion of Kandy within a wreath of ears and lotus, called "Palapeti Vitaya". Below is placed a cup called "Punkalasa" between moon and sun. The coat of arms is crowned by the Buddhist wheel of law, the "Jammachakra".
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


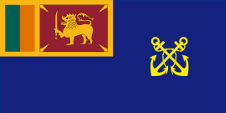
1951–2010,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
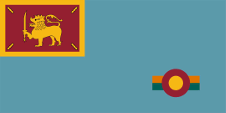
seit/from 2010,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
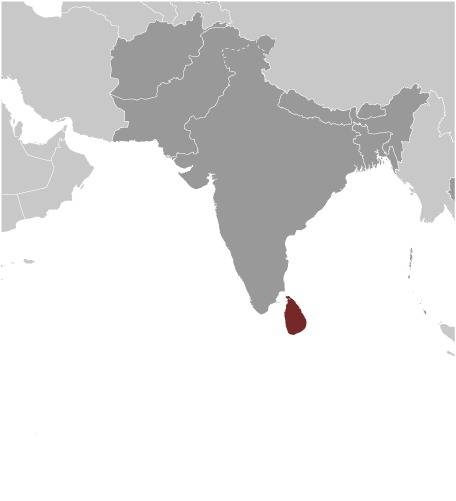
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
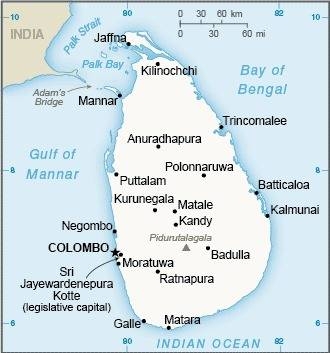
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 25.332 square miles
Inhabitants: 22.000.000 (2023), thereof 75% Singhalese, 11% Tamil, 9% Moors (Arabs), 0.2% Burghers (descendants of Portugese and Netherlanders), 0,2% Malaysians
Religions: 70% Buddhist, 13% Hindu, 10% Muslim, 6% Roman Catholic, 1% Protestant
Density of Population: 868 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Colombo, 752.993 inh. (2011)
Seat of government: Kotte, 107.925 inh. (2012)
official Languages: Singhalese, Tamil
other Languages: English
Currency: 1 Sri Lanka Rupee (LKR, SLR) = 100 Sri Lanka Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 5,5 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

Antiquity · Ceylon Island is known in the Roman Empire as Taprobane, in the buddhist India it is later called Sihaladipa
6th century B.C. · Singhalese from India conquer Ceylon, push aside of the native population of Wedda
3rd century B.C. · onset of the immigration of Tamils from India, later even right invasions
247 B.C. · introduction of Buddhism
10th–15th century A.D. · in the north of Ceylon arise Tamil kingdoms
15th century A.D. · in the south arises the Singhalese kingdom of Kandy (Kingdom of Udarata)
15th of November 1505 · the Portugese seafarer Lourenço de Almeida debarks in Ceylon (Singhalese Kingdom of Kotte) and subordinates it under Portugese supremacy, erection of the fortification of Colombo
1518 · the Portugese make Colombo to the capital of the Kingdom of Kotte
27th of May 1597 · the King of Kotte dies without descendants, the heritage goes to the King of Portugal
1619 · the Portugese conquer Jaffna in the north and rule now over whole Ceylon (Ceilão), the island ist administered from Goa in India
1639–1640 · the Dutch debark in the east and south of the island and establish on behalf of the Dutch East India Company bases (Trincomalee, Batticaloa, Galle) and push later gradually forward in direction of Colombo
1656 · the Dutch conquer Colombo, the Portugese retreat to Jaffna
1658 · the Dutch conquer Jaffna and rule now over nearly whole Ceylon (except the Kingdom of Kandy in the central mountainous region)
1765 · the Dutch rule momentary over the Kingdom of Kandy
1782 · the British rule in Trincomalee
1782–1784 · the Frenchman rule in Trincomalee
1795 · the British East India Company debarks in the east and north of the island and conquers Trincomalee, Batticaloa and Jaffna
1796 · the British East India Company conquers Colombo and rules now over nearly whole Ceylon (except the Kingdom of Kandy in the middle mountains), the island is administered from Madras in India
1802 · Ceylon becomes a British crown colony
1815–1817 · the Kingdom of Kandy becomes conquered and affiliated to the British crown colony of Ceylon until October 1818
4th of February in 1948 · United Kingdom grants Ceylon the independence, Ceylon remains in the British Commonwealth of Nations
1955 · Ceylon becomes member of the UNO
22nd of May 1972 · Ceylon becomes republic, proclamation of the Republic of Sri Lanka
7th of September 1978 · new constitution, Democratic Socialistic Republic of Sri Lanka
1983–1987 · civil war between Tamils and Singhalese, the Tamils claim independence for a Tamile state "Tamil Eelam"
1987 · peace treaty between the government of Sri Lanka und the Tamil LTTE-militia, Indian troops observe the peace (LTTE = Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam)
1988 · the Tamil militia attack the Indian troops
1990 · the Indian troops leave the island
1990–1995 · civil war between governmental troops and Tamils, Jaffna (the capital of the Tamils) becomes conquered, the LTTE-militia disclaims for demands of autonomy areas
1996 · continuation of the fights between governmental troops and Tamils
2009 · complete military victory of Sri Lankan government troops over the LTTE-militia, end of armed Tamil separatism
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

The island of Ceylon has had many different names and was named by various peoples. The Romans called it "Taprobane". In the Buddhist religious language Pali it was called "Sihaladipa", by the Hindus "Sinhala" (kingdom of lions) and by the Arabs "Serendib" (lion island). The name "Ceylon" is of European origin and was probably created by changing the Hindi word "Sinhala" to the Portuguese name "Ceilão". The Dutch and British called it finally "Ceylon". The name "Sri Lanka", which has been used for the state on the island of Ceylon since 1972, is of Sinhalese origin (Tamil: "Ilankai") and means "radiantly beautiful country".
Source: Wikipedia (DE), Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()
































![]()
