mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- parliamentary monarchy
- own name: Koninkrijk der Nederlanden
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Flag History
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Provinces of Netherlands

National, merchant and naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






Merchant flag for naval reserve officers,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



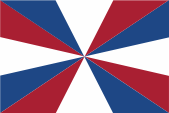
Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Civil jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Differentiational flag for pilot's vessels,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Customs flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Royal flag,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Consuls,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




Flag for admirals and Field Marshalls,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Lieutenant-Admirals,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Vice-Admirals,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Rear-Admirals,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Commodores,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World





Pilot flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is:
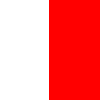 Pilot on board
Pilot on board
 Call for Pilot
Call for Pilot




to 1930,
Flag for Governors of the Netherlands colonies,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1930–1962,
Flag for Governors of the Netherlands colonies,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



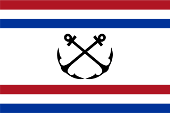
1931-1957,
Flag of the Minister of Navy,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



1937–2004,
personal standard of Prince Bernhard,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1436–1477,
Flag under the Burgundians,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1556–1581 (in Belgium to 1713),
Flag under the Spanish Habsburgs,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1559–1581,
unofficial national flag,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen




1572–1581,
unofficial national flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1581–ca.1660,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




ca.1660–1796,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World






1796–1806,
Batavian Republic,
National flag,
Source, by: Tom Lemmens, CC0,
via Wikimedia Commons




1806–1810,
National flag,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen





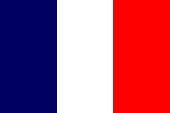
1810–1815,
the Netherlands belong to France,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen






since 1815,
National flag,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen






The Dutch flag is the oldest Republican tricolor of the world. She was introduced during the freedom-fight against Spain under the leadership of the Prince of Orania-Nassau in the year 1579 by the Geuzen (resistance movement). It showed at that time three horizontal dtripes in orange, white and blue, the livery colours (blazon colours) of the Prince of Orania-Nassau. Because of that it is named until today "Prinsenvlag" (→ Prince's Flag). In context with the establishment of the Republic of the United Nethterlands (1581) it was officially adoped as national flag. The orange-coloured stripe was superseded about since 1660 by a red stripe. This colour variant goes back to the "Statenvlag" (→ States Flag), the naval flag of the States-General in the early 17th century. The following explanation is often given as the reason for this change: The flag in orange, white and blue was used at sea and the orange dye was at sea probably not very stable and bad to discern in distances. Red was for this use better suitable and present itself as an alternative. Anyhow became and maintained orange as the national colour of the Netherlanders. In the year 1795 the Netherlands were occupied by French revolutionar troops and there was proclaimed instead of the Netherlands the "Batavian Republic". To have the flag looking more revolutionar or more "French" they officially superseded – what means by resolution or statute – the occasional still used orange-coloured stripe by a red stripe on the 14th of February in 1796. In the now red stripe should have been placed near the pole even an allegorical scene in a white rectangle but this variant accomplished indeed not for the period of the "Batavian Republic". In the year 1806 the Netherlands became the "Kingdom of Holland" and the colour red in the upper stripe was explicitly lawful confirmed. In the year 1810 the "Kingdom of Holland" got directly annexed by France and the Netherlands Tricolor got prohibited. There was to use the French Tricolor. After the withdrawal of the Frenchman (1814) it was allowed to use again the Netherlands flag and the Netherlanders hoisted flags with stripes in orange, white and blue. The red stripe was however officially maintained and in 1816 confirmed by royal decree, in fact on the 19th of February in 1937. This had become necessary again because the Prince's Flag had once more become very popular during the economic crisis of the 1930s. In 1949 the colours were standardised for the first time. In November 1958, the NEN (Dutch Royal Institute for Standardisation), defined the colours, for red as RAL 2002 "Light Vermilion" (HEX #A91F32) and for blue as RAL 5013 "Cobalt Blue" (HEX #1E4785), which would correspond to Pantone 187 and 541. From the Netherlands national colours were developed by tsar Peter the Great (regency: 1682–1725) the panslavic colours, because he made the colours of the Netherlands (blue, white and red) to the colours of Russia (white, blue and red). Under the rule of the Burgundians vessels of Dutch states and provinces showed the red Burgundian Cross with boughes on white ground. In the year 1556 the Netherlands came to the Spanish Habsburgs and they introduced a flag which combines the colours of Spain with the colours of the House of Habsburg. It was horizontally striped and showed the colours red, white and yellow. At the start of the resistance against the Spanish Habsburgs was in use a flag in the underground probably since the year 1559 which was single-coloured red and showed the golden Dutch lion with a sword and a bundle of 17 arrows in the paw. This flag was developed by inversion of colours from the coat of arms of Holland, but the lion received a sword in the hand as a sign of the resistance. The arrows stood for 17 provinces and embodyed the Motto "Eendracht maakt Macht" → "Unity makes strong". After the foundation of the Utrecht Union (1579) they removed those arrows which stood for the under Spanish rule remaining 10 provinces. That flag was after the foundation of the Republic of the United Netherlands (1581) until the Napolèonic times still and only used by the Netherlands Navy and as naval jack.
Source:
Flags of the World,
Das Flaggenbuch,
Wikipedia (EN)



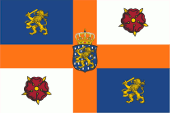
since 1815,
Coat of arms of the Netherlands,
Source: Corel Draw 4


Shield of Arms of the County of Holland
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

1579–1795 (unofficial since 1559),
Coat of arms of the "Utrecht Union" and of the "Republic of the United Netherlands",
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of the Netherlands shows in a blue field coated by golden shingles the golden lion of the Utrecht Union, in the right paw a sword, in the left paw a bundle of seven arrows. Above the shield the Netherlands crown. Shield supporters are likewise golden lions. Below the shield the motto of king William I. "Je Maintiendrai" → "I will persist". The coat of arms was introduced by a decree of King William I. on the 24th of August in 1815. The today's coat of arms of the Netherlands is in this way a combination of the heraldry of the House of Orania-Nassau and of the Utrecht Union. The in 1579 established Utrecht Union adoped a scutcheon which descents from the flag of the anti-Spanish underground fighters. It showed a red shield with a golden lion with a sword and a bundle of 17 arows in the paw. That scutcheon figure was developed by inversion of colours from the coat of arms of the County of Holland. But the lion received a sword in the hand as a sign of resistance. The arrows stood for the 17 provinces of the Netherlands afterward for the 7 provinces of the Utrecht Union. This golden lion was crowned and placed in the year 1815 in the blue blazon – coated by golden shingles – of the House of Nassau. The House of Nassau arised in the year 1160 and splited in the course of times in many lines: e.g. Nassau-Diez, Nassau-Dillenburg, Nassau-Siegen, Nassau-Usingen and Nassau-Weilburg. The coat of arms of the House of Nassau shows a golden lion on a blue field coated by golden shingles. The title of the Princes (Lords) of Orania (French: Orange) came in the year 1530 to the Counts of Nassau-Dillenburg which named themselves Princes of Orania (Haus Nassau-Orania). William the Silent of Nassau-Dillenburg inherited the titel in the year 1544. He became in 1581 as William I. Proconsul of the Netherlands. The heraldry of Orania (Principality of Orange) showed an orange-coloured shield (actually golden) with a blue bugle in it. The County of Holland arised in the 10th century and came in the year 1299 as inheritance to the Counts of Hennegau (Flemish: Henegouwen, French: Hainaut). Those vanish with the death of the last Count of Hennegau and Holland in the year 1345. The coat of arms of the County of Holland showed a red lion on golden ground. The Dutch volunteers, which voluntary fought on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union in the Second World War used as sleeve-insignia a shield in the colours of the country of the Netherlands but passing diagonally from left above to right below.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Avantgarde für Europa,
Wikipedia (DE)

1914–1921,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
1939–1940,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
since 1945,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:

Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 16.040 square miles
Inhabitants: 17.591.394 (2022), thereof 75,4% Dutch, 2,4% Turks, 2,4% Moroccans, 2% Surinamese, 2% Indonesians (mostly Moluccans), 1,9% Germans, 1,3% Polish, 0,8% Antillians
Religions: 20% Roman Catholic, 18% Protestant, 5% Muslim, 54% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 1.097 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Amsterdam, 904.704 inh. (2022),
Regierungssitz: Den Haag (s'Gravenhage), 553.039 inh. (2022),
official Language: Dutch
other Languages: Frysk, German
Currency: 1 Euro (€) = 100 Cent
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

antiquity · settlement by the Germanic tribes of the Batavians, Frysks and Saxons
8th century · conquest by the Franks
843 · at the division of the Frankish Empire comes the Territority of the today's Netherlands to the Kingdom of Lotharingia and since 870 to the East Frankish Empire and since 962 to the German Empire, only the County of Flanders and the County of Artois come to the West Frankish Empire/France
middle ages · evolution of local secular and clerical principalities in the Netherlands (e.g. Duchy of Brabant, Duchy of Limburg, Duchy of Guelders, Duchy of Luxemburg, County of Zealand, County of Hainaut, County of Holland, County of Namur, Diocese of Liège, Diocese of Utrecht)
1345 · the Bavarian House of Wittelsbach acquires the Counties of Hainaut, Zealand and Holland
1384 · the Duchy of Burgund acquires the Counties of Artois and Flanders
1436 · the Duchy of Burgund acquires the Counties of Hainaut, Zealand and Holland as well as the Duchies of Brabant and Limburg
1436–1477 · the Duchy of Burgund acquires the Diocese of Liège and the Duchy of Luxembourg
1477 · death of the last Burgundian Duke (Charles the Audacious), by the marriage of its daughter Maria with Maximilian of Habsburg come the Burgundian Netherlands to the House of Habsburg
1482 · the County of Flanders comes to the House of Habsburg and in this way to the German Empire
1493 · the County of Artois comes to the House of Habsburg and in this way to the German Empire
1507 · appointment of Margaret of Austria as Proconsul General in the Netherlands (to 1530), first common administration for the 17 provinces of the Netherlands
1528 · the Diocese of Utrecht comes to the House of Habsburg
1543 · the Duchy of Guelders comes to the House of Habsburg
1556 · the House of Habsburg divides itself in a Spanish and in a Austrian line, the Netherlands come to the Spanish line (→ Spanish Netherlands), by intensifing religious and financial pressure arise first riotings of the Netherlanders against the Spanish sovereigns
1567 · appointment of the Duke of Alba as Proconsul General of the Netherlands, development of a system of terror, rejection by the freedom movement of the "Geuzen" at land and at sea
1572 · the Geuzen conquer the Town of Brielle
1572–1578 · campaign of the Spaniards for consolidation of the rule, they are only able to protect the ten southern provinces (the today's Belgium), it is not possible to hold the seven northern provinces (the today's Netherlands)
23rd of January 1579 · the seven northern provinces (Holland, Zealand, Utrecht, Guelders, Groningen, Overijssel and Friesland) join together to the "Utrecht Union"
26th of July 1581 · the Utrecht Union declares it's independence from Spain as "Republic of the United Netherlands", formation of a common parliament (Generalstaaten) as supreme authority, the leading Province of Holland gets governed by a "Counsel Pensioner", insertion of William of Orania from the House of Orania-Nassau as Proconsul of the Netherlands, the Netherlands are in this way de facto no longer a part of the German Empire
1584 · assassination of William of Orania, successor is his son Moritz, once more campaigns of the Spaniards to win back the rule
1588 · sinking of the Spanish Armada (130 vessels, 2630 canons, 30 000 man)
1609 · armistice between Spain and the Netherlands
24th of October 1648 · Peace of Westfalia, end of the Thirty Years War in Germany, Spain recognizes with it the independence of the Netherlands
17th/18th century · civil war between troops of the des Counsel Pensioner and the Proconsul, the Netherlands acquire colonial possessions in the whole world
1689 · the Proconsul William III. of Orania becomes King of England,
England and the Netherlands are governed in personal union until 1702
1701–1713 · Spanish War of Succession
1713 · Peace of Utrecht, the former Spanish Netherlands (Belgium) come to Austria (House of Habsburg)
1747 · William IV. of Orania becomes Heritable Proconsul, establishment of the Netherlands monarchy
1780–1784 · colonial war against United Kingdom, the Netherlands have to cede parts of their colonial possessions to United Kingdom
1794 · the Austrian Netherlands (Belgium) become conquered by French revolutionar troops
1795 · the Netherlands become conquered by French revolutionar troops, escape of William V. of Orania, establishment of the "Batavian Republic"
1799–1802 · war against United Kingdom, the Netherlands have to cede once more parts of their colonial possessions to United Kingdom
1806–1810 · the Batavian Republic becomes "Kingdom of Holland" under Ludwig the brother of Napoléon (Louis Napoléon)
1810 · the southern Netherlands (Belgium) and the "Kingdom of Holland" (northern Netherlands) become directly annexed by France
1814 · anti-Napoléonic riot in the southern Netherlands and in the northern Netherlands
29th of March 1815 (Vienna Congress) · establishment of the Kingdom of the United Netherlands by inclusion of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and the Prince Diocese of Luettich, accession to the Throne by William I. of Orania-Nassau, King of the Netherlands and Grand Duke of Luxembourg
18th of November 1830 · the French speaking and catholic Belgium leaves the Kingdom of the United Netherlands because of discrepancies with the Flemish speaking and calvinistic north, the kingdom breaks
1848 · liberal constitution
1890 · the personal union with Luxembourg expires
1914–1818 · First World War, the Netherlands remain neutrally
1922 · new suffrage
10th of May 1940 (Second World War) · the Netherlands become occupied by German troops, government and queen escape to United Kingdom and establish an exile government, 58.000 Netherlanders fight now voluntary on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union, but also arise of a resistance movement
11th of January 1942 · Japan attacks the Dutch East Indies (Indonesia) and occupies large parts of the colony
5th of May 1945 · capitulation of the German War Might in the Netherlands
17th of August 1945 · the Dutch East Indies declare its independence in Batavia as "Republic of Indonesia"
1945–1947 · colonial war of the Netherlands against Indonesia
1947 · Treaty of Linggadjati: recognition of the Republic of Indonesia on the islands Java, Madura and Sumatra
1947–1949 · civil war in Indoniesia, the Netherlands intervene militarily
27th of December 1949 · Treaty of Den Haag: granting of the independence for whole Indonesia, except West Irian and the South Molucca Islands, transformation of the country into a federation, allegiance to the Netherlands crown by the framework of the Netherlands Indonesian Union
24th of March 1950 · the Netherlands grant the independence to the South Molucca Islands
1951 · Belgium, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg and the Netherlands, found the EEC (the later EU)
11th of August 1954 · Indonesia terminates the Netherlands Indonesian Union
1954 · Netherlands Suriname and the Netherlands Antilles get autonomy
31st of December 1962 · West Irian gets transfered from the Netherlands to the UN
1975 · the Netherlands grant the independence to Suriname
1986 · Aruba Island leaves the association of the Netherlands Antilles most appreciably
10th of October 2010 · Netherlands Antilles become dissolved administratively – Curaçao and Sint Maarten become an autonomous country within the Netherlands (like Aruba in 1986), Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba become special municipalities of the Netherlands, but don't belong to any province
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Die Völker der Erde,
Wikipedia (DE)

The name "Netherlands" has German roots and the country received its name because it is just not situated in hilly regions but in "lower land" beyond the mountain ranges, in the lower stretches of the River Rhine. The Netherlands are sometimes named as "Holland" even often by the Netherlanders themselves. That name is derived from the ancient County of Holland which arised in the 10th century and ascended because of its capital Amsterdam to the most important province of the "Utrecht Union" (northern Netherlands) and holded in this way an absolute leading position within the Netherlands. The Province of Holland had in the 16th, 17th and 18th century even an own government. From the year 1806 to 1810 had been summarized the whole northern Netherlands as "Kingdom of Holland" by Napoléon's mercy. In this way the name "Holland" had maintained as denomination for the whole country until today.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Volker Preuß



![]()


























































































