mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Uganda
- presidial republic
- own name:
– Swahili: Jamhuriya Uganda
– English: Republic of Uganda
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• The Kingdoms of Uganda
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1962,
National, state, merchant and war flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1890–1893, British East Africa,
Flag of the British East Africa Company,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1893–1914, British East Africa,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1894–1962,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1894–1962,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1914–1962,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



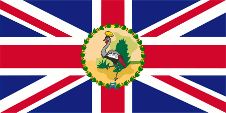
1914–1962,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1962,
National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1962–1963,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




After the Berlin Congo Conference (1884/1885), the Imperial British East Africa Company (IBEA) was founded to develop East Africa economically and colonially. A short time later, the company's flag flew not only over Kenya but also over what is now Uganda, which at the time consisted of many indigenous kingdoms. Due to mismanagement by the IBEA, the British Foreign Office took over the sovereign rights of the company from 1893, which were enforced until around 1903, so that from 1893 the flag of Great Britain flew over the country. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, individual citizens and the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the United Kingdom by using the Union Jack, known as the "Union Flag".
United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper orner.
Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for East Africa, Kenya or Uganda. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
From 1893, the government of British East Africa (also in Uganda), as a British colony, used its own blue ensign with a badge in the waving part of the flag. The badge was the retained logo of the British East Africa Company. It showed a sun with 24 rays below the British crown. The badge appeared directly on the flag cloth and was not placed on a white disc. From 1910 Uganda also had a governor. The blue official flag was equipped with a new badge in Uganda in 1914 and in Kenya in 1921. The badge of Uganda was a disc and showed a landscape depiction with a Grey Crowned Crane. This official flag was retained until 1st of March in 1962. On that date, a new flag was introduced, showing three vertical stripes in green, blue and green with golden dividing stripes and a golden Crowned Crane in the centre of the blue field. United Kingdom granted Uganda independence within the Commonwealth on 9th of October in 1962, and the British monarch remained head of state, represented locally by the Governor-General, but only until 9th of October in 1963, when Uganda became a republic. However, the country remained in the Commonwealth.
The current flag was introduced on the occasion of independence. It shows six horizontal stripes in black, yellow, red, black, yellow and red with a white disc in the centre with a Grey Crowned Crane in the middle. Black, yellow and red are the former colours of the Uganda People's Congress, the party that led the country to independence. Red stands for the brotherhood of all people, yellow for the sun, black for the people and for Africa. The Crowned Crane was adopted from the badge of British Uganda. The colours of the flag are presumably based on the British colour system, so that the colour system of the British Ministry of Defence could be valid. This provides for red = Pantone 186 c and for deep yellow = Pantone 116 c.
Source:
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


since 1962,
Coat of arms of Uganda,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

1890–1893, British East Africa,
Badge of the British East Africa Company,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1893–1914, British East Africa,
Badge of the British East Africa/Uganda,
Source, by: Flags of the World
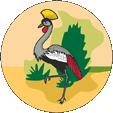
1914–1962,
Badge of Uganda,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The national coat of arms was adopted on 21st of September in 1962 shortly before independence was achieved. It shows a Bantu shield in front of two crossed spears, in its upper part several blue wavy lines (representing the country's many lakes and rivers), in the centre of the shield a golden sun (indicating the country's location below the equator), and in the lower part a drum (symbolising royal power). A gazelle and a crowned crane serve as supporters (shield holders). The shield stands on a green hill with coffee and cotton plants, over which a body of water flows (source of the Nile). Below it, the country's motto in a banner: "For God and my Country" → "For God and my Fatherland". The badge of the British East Africa Company showed a sun with 24 rays below the British crown. It was retained until 1914, after which it was a disc depicting a landscape with a crown crane until 1962.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel #1,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Aircraft Roundel #2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
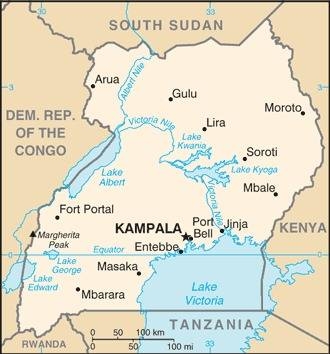
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 93.064 square miles
Inhabitants: 47.200.000 (2022), thereof 18 % Baganda (Bantu), 8 % Banyankole (Bantu), 8 % Bakiga (Bantu), 6 % Lango (Nilote), 4 % Acholi (Nilote), 4 % Lugbara (Nilote), 3 % Banyoro (Bantu), 3 % Batoro (Bantu), 2 % Bahima (Bantu), 6 % Banyarwanda (Bantu), 2 % Karamojong (Nilote)
Religions: 42 % Roman Catholic, 32 % Anglican, 12 % Muslim, 10 % Protestant, 1% Animist
Density of Population: 507 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Kampala, 1.500.080 inh. (2014)
official Languages: Swahili, English
other Languages: div. Bantu, Nilote and Sudan languages
Currency: 1 Ugandan Shilling (USh, UGX) = 100 Cent
Time Zone: GTM + 3 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

On 8th of September in 1967, the historical kingdoms were abolished. The country was only divided into 4 administrative regions, 15 sub-regions and 121 districts. On 24th of July in 1993, the possibility was created to reintroduce the old kingdoms in order to guarantee a certain degree of autonomy, especially cultural autonomy. In a process that continues to this day, some kingdoms have been gradually re-established, with the following major kingdoms existing until 2024: Toro, Busoga, Bunyoro, Buganda and Rwenzururu. The kingdom of Ankole, once an important kingdom, has not yet been recognised. However, several other kingdoms (Padhola) and chiefdoms (Alur, Iteso, Lango) have been officially recognised by the government. The borders of the larger kingdoms run for the most part along the borders of sub-regions.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)
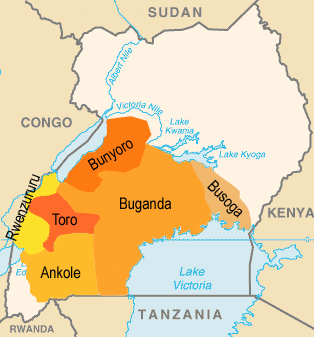
Map: CIA World Factbook, modyfied by: Volker Preuß

since 1993,
Flag of Buganda,
Source, by: Mysid, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

since 1993,
Flag of Bunyoro,
Source, by: World Statesmen

since 1993,
Flag of Toro,
Source, by: World Statesmen

since 1993,
Flag of Ankole,
Source, by: World Statesmen
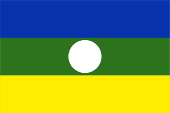
since 2007,
Flag of Rwenzururu,
Source, by: World Statesmen

since 1995,
Flag of Busoga,
Source, by: Jolle, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

9th century · nascence of Bantu tribal states in the south of the country
17th century · the kingdom of Kitwara dominates the region
18th century · the kingdom of Bunyoro dominates the region
19th century · the kingdom of Buganda dominates the region
1858 · the British explorer John Hanning Speke discovers the Victoria Sea and perceives it as the spring-sea of Nile River
1871 · invasion of Egypt troops, the by Nilots inhabited north of the country comes as Equator Province to Egypt
1877 · start of the christian mission
1882 · British troops conquer Egypt
1884/1885 · Congo Conference, the British claims for Buganda become recognized
1885 · the German colonial politician Carl Peters visits Buganda, making contracts
1882–1898 · Mahdi revolt in Sudan, Emin Pascha the governor of the Egypt Equator Province withdraws from 1885 to 1889 to Wadelai in the north of the country
1890 · Uganda Treaty, the Imperial British East Africa Company (IBEA) purchases all German rights in Buganda and starts with the colonization of the region
1893 · the Foreign Office of United Kingdom takes over the administration of the territories in Uganda, from 1895 also in Kenya, due to mismanagement by the IBEA
1893 · the kingdom of Buganda becomes a British protectorate
1894 · establishment of the Protectorate of Uganda
1896 · the kindoms of Toro and Bunyoro become British protectorates, Buganda, Toro and Bunyoro become connected to Uganda
1900 · the Kingdom of Ankole becomes a British protectorate
1900 · immigration of Indians (today 0,5% of the population)
1st of April in 1905 · Uganda gets separated from British East Africa and becomes an individual colony
to 1910 · the tribal territories in the southwest (Chiga, Mpororo), north (Lango, Madi, Lugbara, Alur) and east (Kumam, Teso, Basoga, Bagishu) become British protectorates
to 1920 · the tribal territories in the northeast (Acholi, Karamojong) become British protectorates
1946 · anti British agitations
1949 · anti British agitations
1953 · the king of Buganda claims more freedom, anti British agitations
1958 · first elections, boycott in the kingdom of Buganda
1960 · anti monarchistic agitations in Buganda
30th of December 1960 · Buganda declares unilaterally its independence and the withdrawal from the British protectorate of Uganda, resistance of the tribal territories
1961 · elections, new constitution
1st of March 1962 · Great Britain grants self-administration (inner autonomy)
June 1962 · Uganda Conference, agreement about a federative structure of the country
9th of December 1962 · Great Britain grants the independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations
9t of December 1963 · Uganda becomes republic, president becomes the King of Buganda
1966 · Milton Obote becomes president
8th of September 1967 · the kingdoms become abolished
25th January 1971 · military coup d’état by Idi Amin, deposition of Obote
1979 · expulsion of Amin by troops of Tanzania, the country remains occupied by troops of Tanzania until 1981
1980 · elections, Milton Obote becomes president again
1985 · civil war, Obote goes in exile, new government under Tito Okello
1987 · civil war
24th of July 1993 · the kingdoms become re-established
1995 · new constitution
1996 · first free president's elections, Yoweri Museveni becomes president
1997 · troops from Kongo-Kinshasa operate in Uganda
12th of March 2001 · president's elections, Yoweri Museveni becomes president again
2010 · regional and partial calming of the civil war
2011 · riots
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß

The name "Uganda" derives from the Kingdom of Buganda, the bigest and mightyest of the four kingdoms in the country. "Buganda" means "Land of the Ganda", and Ganda means "people". The Baganda are the bigest Bantu tribe in the country with 17% of the population.
Source:
Wikipedia (EN), Atlas der wahren Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()


































