
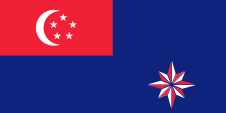
The today’s flag of Singapore was introduced on 3rd of December in 1959, well some month after United Kingdom granted the full self-government to the State of Singapur within the framework of the British Commonwealth of Nations. It shows two horizontal stripes in red and white, as well as a white half-moon and a circle of five white five-pointed stars in the red stripe near the pole. That emblem has nothing to do directly with the Islam, because the half-moon stands for the rise of the country respectively for the young age of the nation. The stars represent the five ideals of the country: democracy, peace, progress, justice and equality. Red stands for the brotherliness of the human beings in the whole world, white for virtue and purity, however red and white are also the traditional colours of the Malays. The use of the flag was and is subject to extremely strict regulations, violations of which are rigorously punished and fined. The government and the people are trying to revise these rules so that the inhabitants can develop a normal patriotic relationship with their flag. The extremely strict rules were revised in 2004 and 2006 and finally implemented in a new law, the National Symbols Bill, which came into force on 1st of August in 2023. This law also stipulates that the red colour of the flag must be Pantone 032.
The flag of the president was also introduced in 1959, however at that time (Singapore was still none republic) for the chief of state, the Yang di-Pertuan Negara. It was taken over in 1965 for the president of the republic. The flag shows the drawing of the blazon of the country, is therefore single-coloured red with a white half-moon and a circle of five white five-pointed stars. In difference to the national flag the emblem on the coat of arms in turned in 90 degrees. The merchant flag was introduced not until the 6th of September in 1966, because to differentiate better the merchant ships of Singapore from those of the neighbouring Indonesia. It is single-coloured red with the moon-stars-emblen in white within a white ring in the middle of the flag.
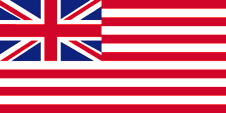
The changeable history of Singapore is very good to see in the here used flags: In the 18th century Singapore belonged to the Sultanate of Linga, and there will have been used the black flag of Lingga, since 1818 with a white upper staff quadrant. As Singapore was selled in 1824 to the die British East India Company, here was used its flag respectively the British Union Jack. The flags of the East India Company showed since the beginning of the 17th century white and red stripes, to differentiate better its ships from the other British ships. In the year 1867 the Straits Settlements – to which Singapore belonged – became a British crown colony. For that was introduced an official flag how it was usual at that times for British colonies. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
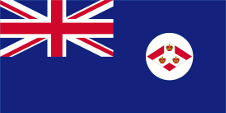
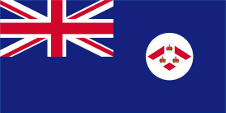
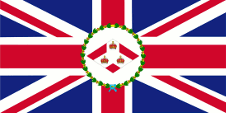
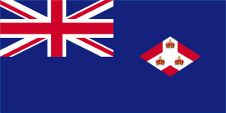
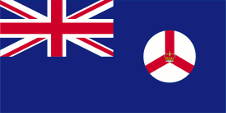
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The badge of the Straits Settlements was a red rhombus with a white shaft on which were layed down three crowns. That stood for the three places of Penang, Malacca and Singapore. On land, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At sea, the British citizen was thus provided with the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were allowed by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea.
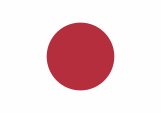
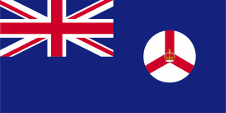
In the times of the Japanese occupation (1942–1945) was used the flag of Japan. In the year 1946 the Colony of the Straits Settlements was dissolved and Singapore became an own British crown colony. As official flag was now used – like it was usual in British colonies – a Blue Ensign, but it showed a new designed bagde in the flying end. It was a white round disk with a red shaft and a British crown in it. On 3rd of December in 1959 finally was introduced the today’s flag and also maintained after the independence in the year 1963. But Singapore belonged from 1963 to 1965 to the Federation of Malaysia and there dominated its flag in passing.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


1946–1952,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D)

1952–1959,
Badge of the Straits Settlements,
Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D)

Coat of arms of Singapore,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms was introduced on 11th of November in 1959, well some month after United Kingdom granted the full self-government to the State of Singapore within the framework of the British Commonwealth of Nations. It shows a single-coloured red blazon with a white half-moon and a circle of five white five-pointed stars. That emblem has nothing to do directly with the Islam, because the half-moon stands for the rise of the country respectively for the young age of the nation. The stars represent the five ideals of the country: democracy, peace, progress, justice and equality. Red stands for the brotherliness of the human beings in the whole world, white for virtue and purity, however red and white are also the traditional colours of the Malays. Supporters of the shield are a lion and a tiger. The lion stands for Singapore itself, because Singapore means "lion's town". The tiger is the scutcheon animal of Malaya and he remembers the former connection with Malaysia. Below the scutcheon a blue banner with the motto "Majulah Singapura" → "May Singapore prosper". During the affiliation of Singapore to the Federation of Malaysia the coat of arms remained unchanged, just as the flag.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


1968–1973,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1973–1990,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

since 1990,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
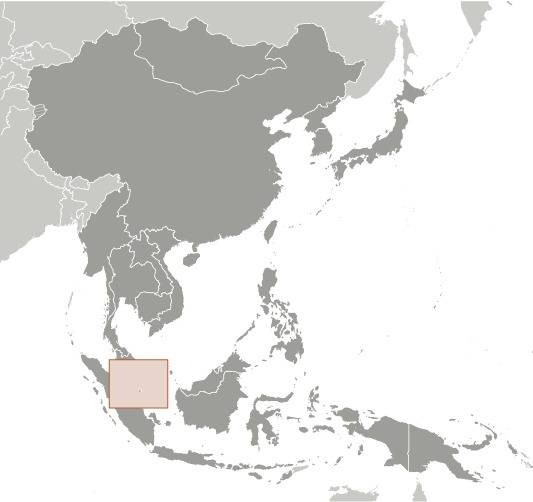
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
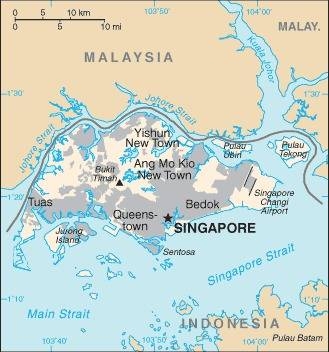
Source: CIA World Factbook
Malaysia and Singapore:
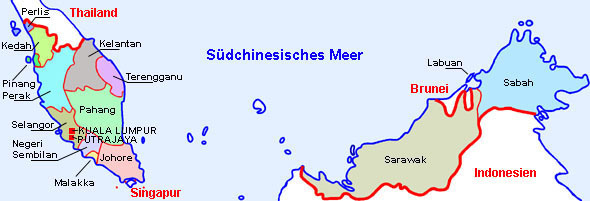
Source: Volker Preuß
Malaya:
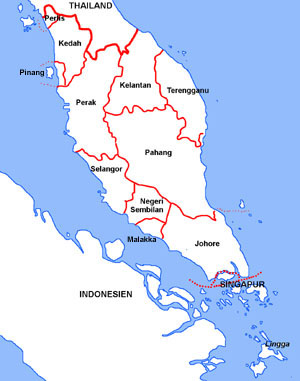
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: 281 square miles
Inhabitants: 5.685.600 (2020), davon 77% Chinese, 14% Malays (Malaysians), 8% Indians
Religions: 33% Buddhist, 19% Christian, 14% Muslim, 10% Daoist, 5% Hindu, 18% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 20.200 inh./sq.mi.
official Languages: Malay, English, Chinese, Tamil
Currency: 1 Singapore Dollar (SGD, S$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 8 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

3rd century · first mention of a settlement named Pu Luo Chung at the place of the today’s Singapore
7th century · onset of the settlement by Hindu Malays from the Kingdom of Shrividjaja (in the today’s Indonesia)
1160 · foundation of the town of Temasek by Hindu Malays at the place of the today’s Singapore
1299 · a prince from Madjapahid (in the today’s Indonesia) gives the place of Temasek the name Singapura (lion's town)
1377 · troops from Madjapahid destroy the town
15th–18th century · Singapore becomes embroiled in the struggles between Siam (today’s Thailand) and the Empire of Madjapahid, the insignificant town is ruled by merchants, pirates and sultans, finally the town belonged to the Sultanate of Lingga
1819 · Sir Stamford Raffles from the British East India Company establishes on Singapore Island an agency
3rd of August 1824 · Sir Stamford Raffles and John Crawfurd purchase Singapore Island from the Sultan of Lingga for the British East India Company
14th of August 1826 · Singapore becomes joined with Penang and Malacca to the colony of the "Straits Settlements" under the supremacy of the British East India Company
1832 · the seat of government of the Straits Settlements becomes transfered from Penang to Singapore
1858 · the administration of the Straits Settlements becomes handed over to British India
1st of April 1867 · the Straits Settlements become a British crown colony
15th of February 1942 · Singapore becomes conquered by Japanese troops in the Second World War
12th of September 1945 · capitulation of the Japanese troops, return of the British, British military government
1st of April 1946 · the end of the Straits Settlements: Penang and Malacca become affiliated to the Malay Union (Malaya), but Singapore becomes an own British crown colony
1948 · state of emergency
1951 · municipal self administration
1955 · United Kingdom grants limited self government
May 1959 · first elections for parliament, new constitution
3rd of June 1959 · United Kingdom grants the "State of Singapore" full self government within the framework of the British Commonwealth of Nations
1962 · plebiscite, majority for an union with the coming Federation of Malaysia
31st of August 1963 · United Kingdom grants Singapore the independence
16th of September 1963 · Singapore joines with Malaya, Sarawak and Sabah to the Federation of Malaysia, the Federation of Malaysia powers strong malaysian-nationalist politics and there arised problems with the by Chinese predominated City of Singapore
1964 · riots
1965 · riots
9th of August 1965 · Singapore leaves the Federation of Malaysia
21st of September 1965 · Singapore becomes member in the UNO
22nd of December 1965 · new constitution as "Republic of Singapore"
1995 · excitements and differences with the Philippines
1998 · excitements and differences with Malaysia
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen

The name "Singapore" was awarded to the town Temasek in the year 1299 by a prince from the Empire of Madjapahid in the today’s Indonesia. The word "Singapur" contains the both Sanskrit words "Simha" and "Pur", Singapore is the "Lion's Town".
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen


![]()

































![]()
