|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
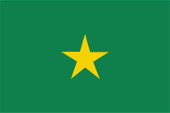
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1958–1959, |
 |
1959–1960, |
Die
heutige Flagge Senegals wurde am 19.08.1960, nach anderen Quellen erst im
September 1960 offiziell eingeführt. Sie zeigt drei senkrechte Streifen in
den panafrikanischen Farben Grün, Gelb und Rot. Im gelben Mittelstreifen
befindet sich ein grüner fünfzackiger Stern. Er steht
|
The
today’s flag of Senegals was officially introduced on 19th of August in
1960, by other sources not until September 1960. It shows three vertical stripes in the pan-african colours green, yellow and red. In the yellow middle stripe is placed a green five-pointed star. It stands
|
Für die
Bedeutung der Farben gibt es unterschiedliche Interpretationen:
|
About the
meaning of the colours exist different interpretations:
|
| Am 25.11.1958 wurde Senegal eine autonome Republik innerhalb der Französischen Gemeinschaft (Communauté Française), und führte zunächst eine grüne Flagge mit einem gelben Stern ein. | On 25th
of November in 1958 Senegal became an autonomous republic within the French
Community (Communauté Française) and introduced initially a green flag with a yellow star. |
| Ab dem 04.04.1959 bildete Senegal mit dem ehemaligen Französisch-Sudan (Mali) die Mali-Föderation. Dieser Staat wurde am 20.06.1960 unabhängig, und führte eine grün-gelb-rot senkrecht gestreifte Flagge mit dem "Kanaga" (Mali-Ideogramm, stilisierter Schwarzer) im gelben Feld. Zwei Monate später verließ Senegal die Föderation und wurde eine souveräner Staat. Das Mali-Ideogramm wurde wenig später von der Flagge entfernt durch einen grünen Stern ersetzt. | Since the 4th of April in 1959 Senegal formed together with the former French Sudan (Mali) the Mali Federation. This state became independent on 20th of June in 1960 and used a green-yellow-red vertical striped flag with the "Kanaga" (Mali Ideogram, stylized Black) in the yellow field. Two month later Senegal left the federation and became a sovereign state. Few times later the Mali Ideogram was removed from the flag and was substituted by a green star. |
| Der Stern soll symbolisieren, dass Senegal allen fünf Kontinenten offen steht. | The star should symbolize that Senegal is opened to all five continents. |
| Die Präsidentenflagge hat das gleiche Design wie die Nationalflagge, zeigt jedoch zusätzlich die Initialen des Präsidenten in schwarz, oft je einen Buchstaben zu beiden Seiten des Sterns. | The flag of the president has the same design like the national flag, but shows further the initials of the president in black, mostly ever one letter to both sides of the star. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind wahrscheinlich nicht exakt definiert. Verschiedentlich lassen sich folgende Definitionen finden: Grün = Pantone 361, Gelb = Pantone 116, Rot = Pantone 186. |
The colours of the flag are probably not exactly defined. The following definitions can be
found from time to time: Green = Pantone 361, Yellow = Pantone 116, Red = Pantone 186. |
| Die Farben Grün, Gelb und Rot sind die panafrikanischen Farben. Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische und auch amerikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen, steht für die politische Einheit Afrikas, ja aller Schwarzen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. | The colours green, yellow and red are the Pan-African colours. The Pan-African-Movement had its beginnings perhaps in 1900, which wants to emphasize the common goals of all black people. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, which are used by many African and even American countries in their flags after independence, stands for the political unity of Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin, the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa, apply. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D), Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
| Wappen – Coat of arms: | |
 |
Wappen Senegals – coat of arms of Senegal, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen wurde im Dezember 1965 eingeführt. Es zeigt einen gespaltenen Schild. In der linken Hälfte einen goldenen Löwen auf rotem Grund - er steht für Stärke - in der rechten Hälfte ein Baobab (Johannisbrotbaum), als typischer Vertreter der Pflanzenwelt des Senegal und im unteren Teil einen grünen Wellenbalken. Er steht für den Senegal-Fluss, die Lebensader des Landes. Auf den silbernen Spruchbänden das Motto des Landes in französischer Sprache: "Un Peuple, Un But, Une Foi" → "Ein Volk, ein Ziel, ein Glaube". | The coat
of arms of Senegal was introduced in December 1965. It shows a clefted
shield. In the left half a golden lion on red ground – It stands for
strength – in the right half a Baobab (carob tree) as a typical substitute
of the flora of Senegal and in the lower part a green wave-line. It stands
for the Senegal River the lifeline of the country. On the silvery banners
the motto of the country in French language: "Un Peuple, Un But, Une Foi" →
"One People, One Goal, One Faith". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
interaktive Landkarte – interactive Map: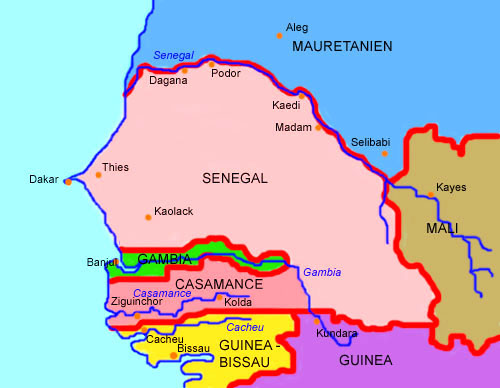 Landkarte/Map: Volker Preuß |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 500
v.Chr. · der karthagische Seefahrer Hanno umsegelt das Kap Verde 900 n.Chr. · Herausbildung lokaler Stammesstaaten, so der Staat der Tekrur (Toucouleur) an der Mündung des Senegal-Flusses, der Staat der Wolof im Westen des heutigen Senegal, der Staat Futa Toro (Fulbe) im Osten des heutigen Senegal 11. Jahrhundert · Islamisierung 14.–15. Jahrhundert · Teile des heutigen Senegal gehören zum Staat Mali 1364 · normannische Seefahrer erreichen den Senegal-Fluss und umsegeln das Kap Verde 1446 · der portugiesische Seefahrer Diniz Fernandez umsegelt das Kap Verde, in den Folgejahren errichten portugiesische Händler südlich von Kap Verde Handelsposten und Stützpunkte (Beziguiche, Portudal, Rio Fresco und Joala) ca. 1600 · Portugal zieht sich von Kap Verde zurück, die Siedlungen verfallen 1621 · die Niederlande errichten auf der die Insel Goree (Ngor) bei Kap Verde einen Stützpunkt 1626 · Frankreich errichtet an der Mündung des Flusses Senegal den Stützpunkt Saint Louis 1638 · Saint Louis wird durch ein Fort gesichert 1640 · Frankreich errichtet am Fluss Senegal den Stützpunkt Podor 1672 · Gründung der "Compagnie de Sénégal" 1677 · Frankreich besetzt die Insel Goree, die Niederländer werden vertrieben 1693 · Großbritannien besetzt kurzzeitig die französischen Stützpunkte am Fluss Senegal 1697 · Frankreich errichtet am Fluss Senegal den Stützpunkt Madam 1758–1779 · Großbritannien besetzt die französischen Stützpunkte am Fluss Senegal 1800–1817 · Großbritannien besetzt die französischen Stützpunkte am Fluss Senegal ca. 1830 · die Franzosen dringen in das Hinterland ein und errichten weitere Stationen und Stützpunkte an der Küste, im Hinterland und am Gambia-Fluss 1854 · die französischen Besitzungen zwischen Senegal-Fluss, Kap Verde und dem Gambia-Fluss werden zu "Senegambien" zusammengefasst und erstmals einem Gouverneur (General L. Faidherbe) unterstellt 1857 · Gründung der Stadt Dakar 1870–1883 · der militärische Widerstand im Hinterland wird gebrochen, die französischen Truppen bewegen sich südlich des Senegal-Flusses allmählich ostwärts mit dem Ziel den Fluss Niger im heutigen Mali zu erreichen, 1880 wird Bafulabe erobert, 1881 Kita, 1883 erobern die französischen Truppen Bamako am Niger 1885 · Eröffnung einer Eisenbahnlinie zwischen Saint Louis und Dakar 1889 · Grenzvertrag mit Großbritannien am Gambia-Fluss 1895 · Bildung des Generalgouvernements Französisch-Westafrika 1902 · Bildung der Kolonialföderation Französisch-Westafrika bestehend aus: 1939–1945 · zweiter Weltkrieg, Senegal untersteht anfänglich der mit dem Deutschen Reich verbündeten französischen Regierung in Vichy 25.11.1958 · Senegal wird nach einer Volksabstimmung kein unabhängiger Staat, sondern autonome Republik innerhalb der Französischen Gemeinschaft (Communauté Française) 04.04.1959 · Senegal vereinigt sich mit dem ehemaligen Französisch-Sudan (Mali) zur Mali-Föderation innerhalb der Französischen Gemeinschaft 20.06.1960 · Senegal verlässt die Mali-Föderation und wird ein unabhängiger Staat 1960–1980 · Herrschaft des Präsidenten Léopold Sédar Senghor 1963 · Senegal wird präsidiale Republik, Senghor übernimmt auch das Amt des Ministerpräsidenten 1965 · umfassendes Kooperations-Abkommen mit Gambia 1966–1976 · Einparteiensystem 1980–2000 · Herrschaft des Präsidenten Abdou Diouf 1982–1989 · Senegal und Gambia sind in der Konföderation Senegambia verbunden (gemeinsame Militär- Wirtschafts- und Finanzpolitik) 1989 · kriegerische Auseinandersetzungen mit Mauretanien 1990–1993 · Casamance-Konflikt, die Region Casamance im Süden von Senegal versucht sich von Senegal zu trennen 1995 · erneute Gefechte in der Casamance 2000 · erneute Gefechte in der Casamance, Spannungen mit Mauretanien |
| 500 B.C.
· the Carthagian seafarer Hanno sails round Cape Verde 900 A.D. · evolution of local tribal states, e.g. the State of the Tekrur (Toucouleur) at the mouth of the Senegal River, the State of the Wolof in the west of the today’s Senegal, the State of Futa Toro (Fulbe) in the east of the today’s Senegal 11th century · islamization 14th–15th century · parts of the today’s Senegal belong to the Mali-State 1364 · Norman seafarers reach the Senegal River and sail around Cape Verde 1446 · the Portugese seafarer Diniz Fernandez sails around Cape Verde, in the afteryears establish Portugese merchants trading stations and bases southern Cape Verde (Beziguiche, Portudal, Rio Fresco and Joala) ca. 1600 · Portugal withdraws from Cape Verde, the housing estates decay 1621 · the Netherlands establish on Goree Island (Ngor) near Cape Verde a base 1626 · France establishes near the mouth of Senegal River the base of Saint Louis 1638 · Saint Louis becomes protected by a fort 1640 · France establishes at the Senegal River the base of Podor 1672 · foundation of the "Compagnie de Sénégal" 1677 · France occupies Goree Island, the Dutchman become banished 1693 · United Kingdom occupies momentary the French bases at Senegal River 1697 · France establishes at the Senegal River the base of Madam 1758–1779 · United Kingdom occupies the French bases at Senegal River 1800–1817 · United Kingdom occupies the French bases at Senegal River ca. 1830 · the Frenchmen invade the hinterland and establish further stations and bases at the coast, in the hinterland and on Gambia River 1854 · the French possessions between Senegal River, Cape Verde and the Gambia River become summarized to "Senegambia" and subordinated for the first time under a governor (General L. Faidherbe) 1857 · foundation of the town Dakar 1870–1883 · the military resistance in the hinterland becomes broken, the French troops move southern of Senegal River gradually eastwards to reach the Niger River in the today’s Mali, 1880 conquest of Bafulabe, 1881 conquest of Kita, 1883 conquer the French troops Bamako at Niger River 1885 · opening of a railroad line between Saint Louis and Dakar 1889 · border treaty with United Kingdom around the Gambia River 1895 · establishment of the Government General French West Africa 1902 · establishment of the colonial federation of French West Africa consisting of: 1939–1945 · Second World War, Senegal is initially subordinated to the with the German Empire allied French government in Vichy 25th of November 1958 · Senegal becomes after a referendum no independent state but an autonomous republic within the French Community (Communauté Française) 4th of April 1959 · Senegal unites with the former French-Sudan (Mali) to the Mali-Federation within the French Community 20th of June 1960 · Senegal quits the Mali-Federation and becomes an independent state 1960–1980 · rule of the President Léopold Sédar Senghor 1963 · Senegal becomes a presidial republic, Senghor takes also over the function of the premier 1965 · extensive agreement about cooperation with Gambia 1966–1976 · single party system 1980–2000 · rule of the President Abdou Diouf 1982–1989 · Senegal and Gambia are connected in the Senegambia Confederation (joint military, economic and financial policy) 1989 · military quarrels with Mauritania 1990–1993 · Casamance-Conflict, the region of Casamance in the south of Senegal trys to separate from Senegal 1995 · once more battles in the Casamance 2000 · once more battles in the Casamance, strained relations with Mauritania |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
| Der Landesnamen "Senegal" geht auf den Senegal-Fluss zurück. Er ist die Lebensader des Senegal und sein Tal war die Wiege der Kultur dieses Landes. Senegal heißt in der Sprache der Wolof "Der Schiffbare". | The name of the country "Senegal" has its roots in the Senegal River. He is the lifeline of Senegal and its valley was the cradle of culture of this country. Senegal means in the language of the Wolof "the navigable". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |