mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Kiribati
- presidial republic with initial stages of parliamentarism
- own name: Ribaberikin Kiribati
- former name: Gilbert Islands
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• Dependencies
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4







1893–1916,
Gilbert Islands Protectorate,
Flag of the British Resident Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1916–1969,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1916–1979,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1916–1971,
Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony,
Flag of the British Resident Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1916–1975,
Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony,
Customs flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1877–1953,
Flag of Western Pacific High Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1953–1971,
Flag of Western Pacific High Commissioner,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



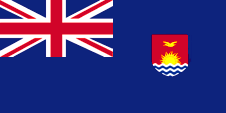
1937–1969,
Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1969–1975,
Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1975–1979,
Gilbert Islands Colony,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1975–1993,
Gilbert Islands & Kiribati,
Customs flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The design of the flag corresponds to that of the national coat of arms and shows a large red field and a frigatebird above a rising sun above three blue-white wavy lines. The frigate bird stands for strength and freedom and the wave lines for the Pacific, in which lie the islands of the state are situated. The flag won in a contest, and was hoisted for the first time on the 12th July in 1979 on occasion of the independence. The colors of the Kiribati flag follow the British BSI standard: Red = 539 - Currant red, Yellow = 355 - Lemon, Blue = 110 - Roundel blue. In the Pantone mixing system, this would correspond to the following values: red = pt 1795, yellow = pt 116, blue = pt 294. In British colonial times was hoisted the usual blue official flag (Blue Ensign) with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant and the emblem of the country in the flying part of the flag. The Union Jack pointed to the connexions to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other. Since 1916 the Ellice Islands and the Gilbert Islands had been united to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony. From 1937 over the separation of the Ellice Islands in the years 1975/1976 and until the independence was in use a Blue Ensign with the blazon of the colony. It showed an yellow frigate bird (symbol for strength and freedom) on red ground above a rising yellow sun, underneath three wavy blue-white stripes (symbol for the Pacific Ocean, in which the islands are situated).
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (D)


since 1979,
Coat of arms of Kiribati,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1937–1979,
Coat of arms of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The coat of arms of the state - which was awarded the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony on the 1st of May in 1937 - shows exactly like the flag a yellow frigate bird in a red field above a rising yellow sun, underneath three wavy blue-white stripes. The golden banner under the coat of arms carrys since 1979 the motto "Te Mauri Te Raoi ao Te Tabomoa" ("Health, Peace, Prosperity ", by an other translation "Luck, Peace and Progress"). The previously silvery banner carryed before in two languages (Gilbertese and Tuvalu) the motto "Fear God and honor the King".
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flags of the World

Location:
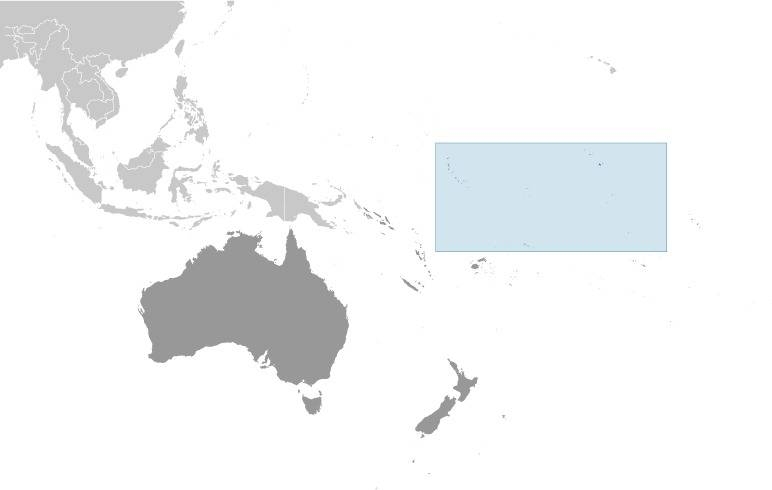
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
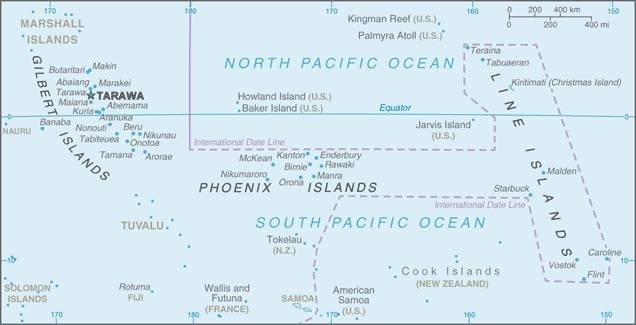
Source: CIA World Factbook
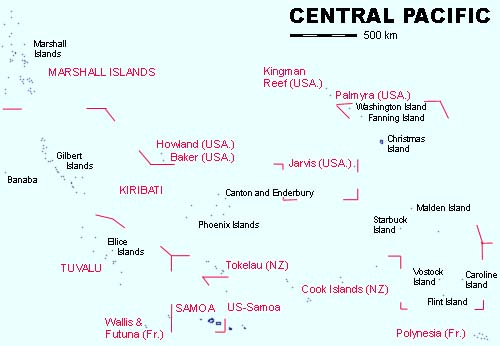
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: 280 square miles, Dependencies (← click here)
Inhabitants: 119.438 (2020), thereof 96% Mikronesians (Gilbertese), 1,2% Europeans, 1% Polynesians, 0,5% Chinese, Banabaians, Tuvaluans
Religions: 59% Roman Catholic, 30% Protestant, 8% other Christian, 2% Bahai
Density of Population: 426 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: South Tarawa (Gilbert Islands), 63.439 inh. (2020)
official Languages: English, Gilbertese (i-Kiribati)
Currencyen: 1 Australian Dollar (AUD) = 100 Cent, 1 Kiribati-Dollar (KID) = 100 Cent
Time Zone: GMT + 12 h to + 14 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

Gilbert Islands
main archipelago of Kiribati
108 sq.mi., 108.331 inh. (2020),
1537 · the Spaniard Grijaloa discovers the Gilbert Islands
1777 · the Briton James Cook explores the Gilbert Islands
1860 · British colonization
1892 · the Gilbert Islands become a British protectorate
1916 · summarized with the Ellice Islands
1979 · as Kiribati independent
Ocean Island (Banaba)
2,5 sq.mi., 333 inh. (2020),
1900 · discovery of phosphate, British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
1981 · claims for independence
Canton and Enderbury
to the group of the Phoenix Islands,
5,4 sq.mi., uninhabited,
initially between USA and United Kingdom vexed archipelago
1939 · formation of a British-US-American condominium
1979 · to Kiribati
Phoenix Islands
10,8 sq.mi., 41 inh. (2020),
1889 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
1995 · resettlement of 1 500 peoples from Tarawa to isles of the Phoenix Islands
Washington Island (Teraina)
to the group of the Line Islands,
5,4 sq.mi., 1.893 inh. (2020),
1889 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
Fanning Island (Tabuaeran)
to the group of the Line Islands,
13 sq.mi., 1.990 inh. (2020),
1889 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
Christmas Island (Kirimati)
to the group of the Line Islands,
149,8 sq.mi., 7.369 inh. (2020),
1777 · dicovered by the Briton James Cook
1888 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1957 · British nuclear tests
1979 · to Kiribati
Malden Island
to the group of the Line Islands,
15 sq.mi., since 1927 uninhabited,
traces of very old population
1864 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1957 · British nuclear tests
1979 · to Kiribati
Starbuck Island
to the group of the Line Islands,
6 sq.mi., since 1920 uninhabited,
1866 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1920 · the Guano quarrying becomes ceased
1979 · to Kiribati
Vostock Island
to the group of the Line Islands,
0,2 sq.mi., uninhabited,
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
Caroline Island
to the group of the Line Islands,
1,5 sq.mi., since 1930 uninhabited,
1795 · dicovered by the Briton W. R. Broughton
1868 · British appropriation
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati
Flint Island
to the group of the Line Islands,
1 sq.mi., since 1930 uninhabited,
1916 · to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
1979 · to Kiribati

1537 · the Spaniard Grijaloa discovers the Gilbert Islands
1568 · the Spaniard Alvaro de Mendana discovers the Gilbert Islands
1606 · the Spaniard Quiros explores the Gilbert Islands
1777 · the Briton James Cook explores the Gilbert Islands
1857 · beginning of the christian mission
1860 · settlement and colonization by the British, establishment of plantations, enslavement of large parts of the population
1888 · British appropriation of the Christmas Island and further outlying islands and archipelagos
1892 · United Kingdom takes possession of the Gilbert Islands, merging them with the Ellice Islands (today's Tuvalu) to form the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Protectorate
1900 · the British discover phosphate on Banaba Island, British appropriation
1916 · the Gilbert and Ellice Islands protectorate becomes a British crown colony
1941–1943 · the Gilbert and Ellice Islands are occupied by Japanese troops
1957 · British nuclear tests near Christmas Island (Kirimati)
1st of October 1975 · separation of the Ellice Islands as an own colony
1977 · United Kingdom grants internal autonomy for the Gilbert Islands
1st of October 1978 · the Ellice Islands become independent under the name Tuvalu
12th of July 1979 · the Gilbert Islands become independent under the name Kiribati
1981 · Banaba Island claims independence from Kiribati
1988 · resettlement of 5 000 peoples from Tarawa to isles of the Line Islands
1995 · resettlement of 1 500 peoples from Tarawa to isles of the Phoenix Islands
1996 · the date-line, which before passed between the Gilbert and the Phoenix Islands, becomes relocated behind the eastern frontier of Kiribati
1996 · joining the UN
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97

The name of the country, which the local inhabitants pronounce as "kiribas", goes back to the name of the "Gilbert Islands", spoken changed and in a native way and polished off linguistically.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()


























