
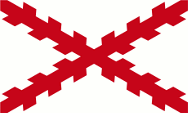
16th century,
The island belongs to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



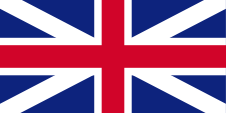
1761–1778,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1778–1784,
Flag of France,
Source, by: Sodacan [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons




1784–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1801–1871,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source by:
World Statesmen





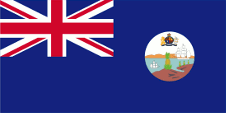
1871–1939,
Leeward-Inseln,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1939–1955,
Windward-Inseln,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen



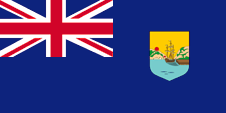
1955–1965,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



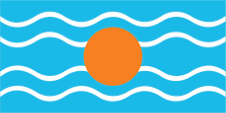
1958–1962,
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1965–1978,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



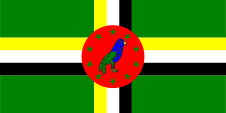
1978–1981,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1981–1988,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




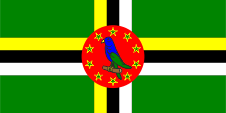
When Dominika became independent on 3rd of November in 1978, a green flag with a three-colored cross (yellow, white and black) was introduced, which had a red disc with ten green stars and a parrot in the middle. The flag was designed by Alwin Bully. In the years up to 1990 there were some changes: 1981; Order of the colors in the cross, the stars have a yellow border, 1988; The parrot is mirrored around a vertical axis and from now on it sits on a small branch. The color green stands for the nature of the island, and the threecolored cross stands for the Christianity and the christian Trinity. Yellow symbolizes the sun and fruitfulness, as well as the Mulattos. White embodys the water and the purity, as well as the white residents of the island. Black allegorys the soil, as well as the residents of African descent. The red disk stood initialy for the socialistic development program of the island. The ten stars in the disk represent the clerical administrative districts of the island. The parrot in the middle of the disk is a Sisserou (Amazon Imperialis), the national symbol of Dominica. He is borrowed from the coat of arms of the state.
Initially Dominica belonged to the British Leeward Islands Colony – later to the British Windward Islands Colony – and became in 1960 a self-contained colony. The national flag was in that times a so called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack pointed out to the connections to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" => civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment => the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other.
The Leeward Islands became awarded an own badge in the year 1871. It showed a pineapple at a coast with two ships. The flag of the Windward Islands carryed an other badge. It showed a fourfold divided shield with the colours red, yellow, green and white, surrounded by a white belt with the inscription "Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", above the British crown. Below a white banner with the motto of the islands: "i pede fausto" => "go with blessed foot". The separate colonies of the Windward Islands had however mostly used their own "Blue Ensigns" with an own badge. The flag of the Windward Islands was almoust used by the government of the colony.
Dominica became awarded an own badge in the year 1955, which was in use on an "Blue Ensign". It showed coastal scenery with a British merchant ship with reefed sails in the foreground and in the background the silhouette of a town at a mountain. Dominica, since 1967 with his own government, used no badge anymore since 1965, but the in 1961 awarded coat of arms of the state.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt


1871–1939,
Badge of the Leeward Islands
Source: Das Flaggenbuch

1939–1955,
Badge of the Windward Islands
Source: Das Flaggenbuch
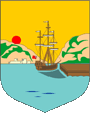
1955–1965,
Shield of Dominica
Source: Flags of the World

Coat of arms of Dominica,
Source:
Corel Draw 4

The today's coat of arms of Dominica shows two Sisserou Birds (Amazon Imperialis) as shield holders, und a quartered blazon. The single fields show regional motives: palm tree, frog, sailing boat and banana tree. Above the shield on a golden-blue torus a golden British lion. Below the shield a maxim-ribbon with the motto of the state in French: "Aprés Bondies c'est la Ter" => "Behind God comes the country".
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt

Location:
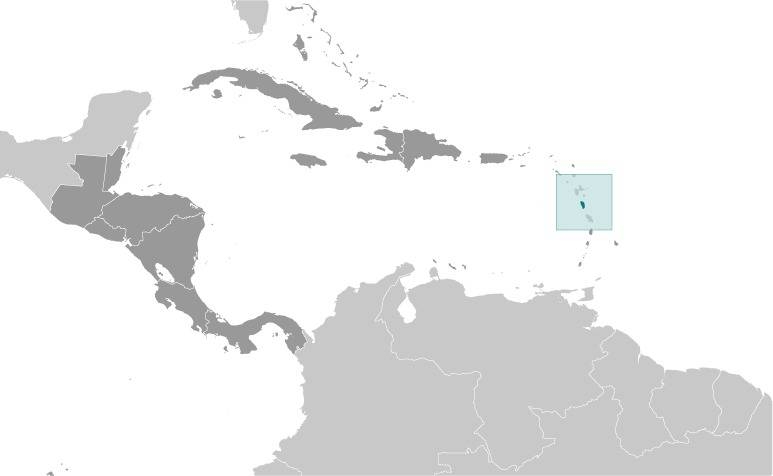
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
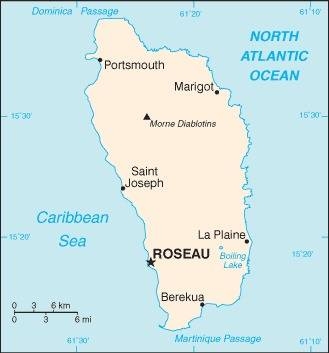
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 290 square miles
Inhabitants: 71.625 (2018), thereof 86% of African descent, 9% Mulattos, 3% Caribs, 1% Europeans
Religions: 80% Roman Catholic, 15% div. Protestant
Density of Population: 272 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Roseau, 14.725 inh. (2011)
official Language: English
other Languages: Creole French (Patois)
Currency: 1 East Caribbean Dollar (EC$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (EN)

5th to 4th millennium B.C. · first human settlement on the island
3rd of November in 1493 · discovered by Columbus
1627 · the Earl of Carlisle claimes the island for England, but there is no colonization
1635 · France lays claim to the island, but there is no colonization
31st of March in 1660 · Agreement between the Caribbean natives, the English and French that the island is left to the Caribs, but in the following years reach a number of French settlers the island
1686 · England and France confirm the status of the island as Carib Territory, but in the afteryears come again French settlers and missionaries on the island
1700 · the British attempt to establish a colony on the island
1748–1761 · the island is officially a neutral territory between United Kingdom and France
6th of June in 1761 · United Kingdom occupies the island
1778 · France occupies the island
1784 · Dominica becomes a British colony again
1833–1940 · Dominica is part of the British colony of the Leeward Islands
1865 · Dominica becomes a Crown Colony
1940–1960 · Dominica is part of the British colony of the Windward Islands
3rd of January in 1958 to 31st of May in 1962 · Dominica is part of the British colony of the "West Indian Federation"
1st of March in 1967 · Dominica becomes a with United Kingdom associated state (internal self-government)
3rd of November 1978 · United Kingdom grants independence
1981 · Attempted coup by the military, as a result of that, the military is abolished with exception of a small special unit, USA and Canada are responsible for national defense since 1996
Source: Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

Columbus discovered the island on a Sunday, the "Day of the Lord", in Latin: "Dies Domini". Hence the name of the island "Isla Dominga" was derived. Later, it was just Dominica.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()


































![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()



![]()



![]()

![]()






