mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Antigua and Barbuda
- parlamentaric monarchy with the British monarch as Head of State
- own name: State of Antigua and Barbuda
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






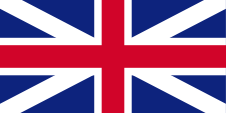
1671–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen






1801–1871,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen





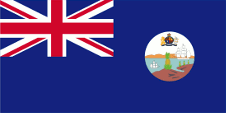
1871–1957,
Leeward Islands,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1957–1967,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



1958–1962,
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Today's flag of Antigua was introduced on the 27th of February, 1967. It won in an idea contest, and was created by Reginald Samuel. The flag shows on a red base an on the top standing two-equal-sided triangle. Above the upside down white triangle a blue bar is positioned, and above it a golden rising sun on a black ground. The triangle symbolizes the ”V” for victory-sign, and the rising sun, the beginning of a new era. Red stands for the dynamism of the people, blue for the hope and the ocean, black for the earth and the African legacy of the people, white for the sand. The colour-triad of yellow, blue and white is to promote tourism: sun, sea and sand.
Initially Antigua belonged to the British Leeward Islands Colony and became in 1960 a self-contained colony. The national flag was in that times a so called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack pointed out to the connections to Great Britain. Great Britain introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other.
The Leeward Islands became awarded an own badge in the year 1871. It showed a pineapple at a coast with two ships. Antigua became awarded an own badge in the year 1957, which was in use on an "Blue Ensign". It showed coastal scenery with a brown palm tree in the foreground and in the background a building on a hill.
Great Britain granted interior self administration on 27th of February in 1967, and Antigua became an autonomous with Great Britain associated state. On the occasion of that fact was introduced the today's flag which finished the tradition of the "Blue Ensigns".
The coat of arms of autonomous Antigua was created by Gordon Christopher, and was awarded to the islands by Queen Elisabeth II of Great Britain on the 16th of February, 1967. The shield of the coat of arms is divided by silvery and blue wave lines, in front of them a stylized mill is a reminder of sugarcane processing. The black head of the shield shows the golden rising sun. On the shield rests a helmet with a torus and helmet blankets, above the torus a golden pineapple, which is surrounded by four red blossoms. The shield holders are two deer native to the island of Barbuda. They stand on a green grassy expanse, which is surrounded by blue and silver wavy stripes. The right deer carries the shaft of the sugarcane, the left one that of Barbuda’s cotton. The silver banner reads in red embroidery the motto ”Each endeavouring, all achieving".
Source: Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
World Statesmen

Location:
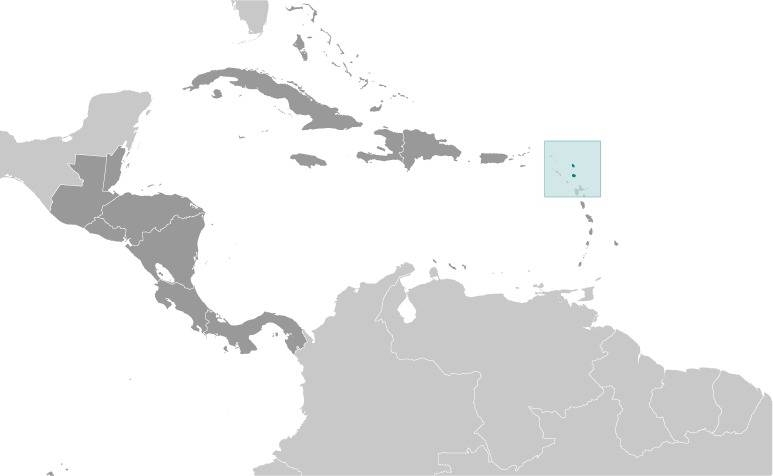
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
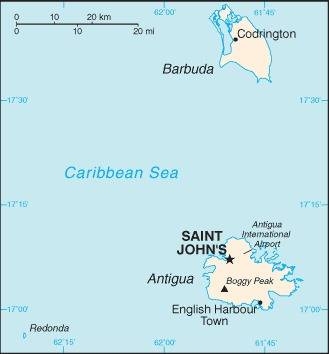
Source: CIA World Factbook
Interactive Map of the Leeward Islands:
Source: Map is Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuss

Area: 171 square miles, thereof Antigua 108 sq.mi., Barbuda 62 sq.mi., Redonda 1 sq.mi.
Inhabitants: 94.700 (2017), thereof 87.3% African descent, 4.7% mixed, 2.7% hispanic, 1.6% white, 2.7% other
Religions: 68.3% Protestant, 8.2% Roman Catholic, 5.9% none
Density of Population: 391 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Saint John's, 22.000 inh. (2013)
official Language: English
Currency: East Caribbean Dollar (XCD, EC-$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source: Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

1493 · discovered by Columbus
1632 · start of the English colonization
1671–1960 · part of the British Colony of the Leeward Islands (except 1816–1833)
1958–1962 · part of the British Colony of the "Federation of the West Indies"
1967 · status of autonomy
1st of November 1981 · independence
Source: World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Antigua" was given to the island in 1493 by Columbus. It means: "The Old". The name "Barbuda" was also given to the island in 1493 by Columbus. It means: "The Bearded".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Wapedia (D)


![]()

















