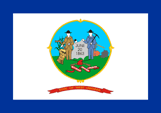
Die heutige Flagge von
Westvirginia wurde am 07.03.1929 eingeführt. Sie zeigt ein einfarbiges weißes, blau
umrandetes Grundtuch, häufig noch durch eine zusätzliche Borte mit roten Fransen
ergänzt. Weiß steht für die Reinheit und Blau für die Union. In der Mitte der Flagge
erscheint, platziert auf einem golden umrandeten Schild, das zentrale Element des
Staatsiegels, ein durch einen Bauern und einen Bergarbeiter flankierten Stein, mit dem
Datum "20.06.1863", der Beitritt des Staates zur USA. Rings um den Stein
befinden sich Symbole der wichtigsten Wirtschaftszweige des Landes: Kornähren,
Maispflanzen, ein Pflug, Amboss und Hammer, ein Haufen Erz. Vor dem Stein eine phrygische
Mütze (Symbol der Freiheit) auf zwei gekreuzten Gewehren. Ein Zeichen dafür, dass die
Freiheit auch mit Waffengewalt verteidigt werden wird. Unterhalb ein Spruchband mit dem
Motto des Landes: "Montani semper liberi" => "Bergbewohner sind immer
frei". Das Wappen ist links und rechts von Rhododendronzweigen bekränzt, die von
einem roten Band zusammengehalten werden. Der Rhododendron ist die Staatsblume von
Westvirginia. Oberhalb des Wappens befindet sich ein rotes Spruchband mit dem Namen des
Landes. Als Westvirginia, als
verfassungswidrige Abspaltung von Virginia, am 20.06.1863 als 35ster Staat der USA
beitrat, wurde bei der Zeremonie eine Flagge verwendet, die der Flagge der USA glich,
jedoch war die blaue Oberecke quadratisch und zeigte einen fünfzackigen Stern, der aus 35
einzelnen weißen Sternen gebildet wurde. In den Folgejahren wurde nur noch die Flagge der
USA benutzt. Am 24.02.1904 wurde
wieder eine eigene Staatsflagge eingeführt. Sie zeigte, wie die heutige Flagge, ein
einfarbiges weißes, blau umrandetes Grundtuch, und in der Mitte der Flagge das zentrale
Element des Staatsiegels, platziert auf einem golden umrandeten, nahezu runden Schild. Auf
einem roten Spruchband erschien unterhalb des Wappens der Name des Landes in goldenen
Lettern. Die Rückseite dieser Flagge zeigte in der Mitte des weißen Feldes drei große
Rhododendronblüten. Am 25.02.1907 wurde Rückseite dieser Flagge offiziell zur
Vorderseite gemacht, und die bisherige Vorderseite zur Rückseite. Dieses Design wurde bis
zu Einführung der heutigen Flagge am 07.03.1929 beibehalten.
The today's flag of
West Virginia was introduced on 7th of March in 1929. It shows a single-coloured white but
blue-edged bunting, often supplemented by an additional border with red fringes. White
stands for purity and blue for the Union. In the middle of the flag appears, placed on a
golden bordered shield, the central element of the state seal, one by one farmer and a
miner flanked stone with the date "June 20th 1863", the date of the joining to
the USA as an own state. Around
the stone are symbols of the country's most important industries: grain corn, corn plant,
a plow, anvil and hammer, a pile of ore. In Front of the stone a Phrygian Cap (the symbol
of freedom) on two crossed rifles. A sign which shows, that freedom will be defended by
force of arms. Beneath a banner with the motto of the country: "Montani semper
liberi" => "Mountaineers are always free".
The emblem is on the left and on the right, crowned by rhododendron branches, held
together by a red ribbon. The rhododendron is the state flower of West Virginia. Above the
emblem a red banner with the name of the country. When West Virginia –
as an unconstitutional secession of Virginia – joined the USA as 35th state on 20th
of June in 1863, was used during the ceremony, a flag that resembled the flag of the
United States, however, the blue upper corner was square and showed a five-pointed star,
which was formed from 35 single white stars. In afteryears was only in use the flag of the
United States. On 24th of February in
1904 was re-established an own state flag. It showed – like the current flag – a
single-coloured white but blue-edged bunting, and in the middle of the flag appeared the
central element of the state seal, placed on a golden bordered, nearly round shield. Below
the shield appeared the name of the country in golden letters on a red banner. The reverse
of this flag showed in the middle of the white field, three large rhododendron blossoms.
On 25th of February in 1907 the reverse of this flag was officially made to the obverse,
and the current obverse became the reverse. This design has been maintained until the
introduction of the today's flag on 7th of March in 1929. |